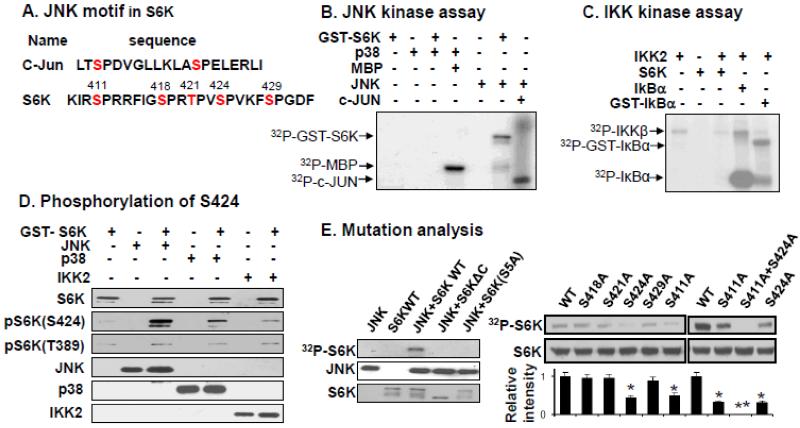
Fig. 2.
S6K phosphorylation by JNK1 in kinase assay. A. JNK1 target sequences in S6K. Amino acid sequence in c-JUN was used as a consensus sequence in the S6K analysis. Five candidates for JNK-sensitive residues are shown in red font in the c-terminal of S6K. B. JNK1 kinase assay. The kinase assay was conducted with purified JNK1 (kinase) and GST-S6K1 (substrate). The phosphorylation was tracked with radioactivity of 32P. C. IKK2 kinase assay. Purified IKK2 and S6K1 were used with 32P. IkBα was an authentic IKK2 substrate. D. Phosphorylation detected with antibody. S424 phosphorylation in S6K was investigated with phosphor-specific antibody to pS6K(S424) after the kinase assay. In the negative control, IKK2 and p38 were used in the kinase assay. The phosphor-specific antibody to pT389 was used in control. E. Mutation analysis of S6K. Mutant proteins were tested in the JNK1 kinase assay and relative strength of 32P signal was quantified (n=3). The experiments were repeated three times with consistent results and representative blots are presented in this figure. * P<0.05, ** P<0.001 over control.