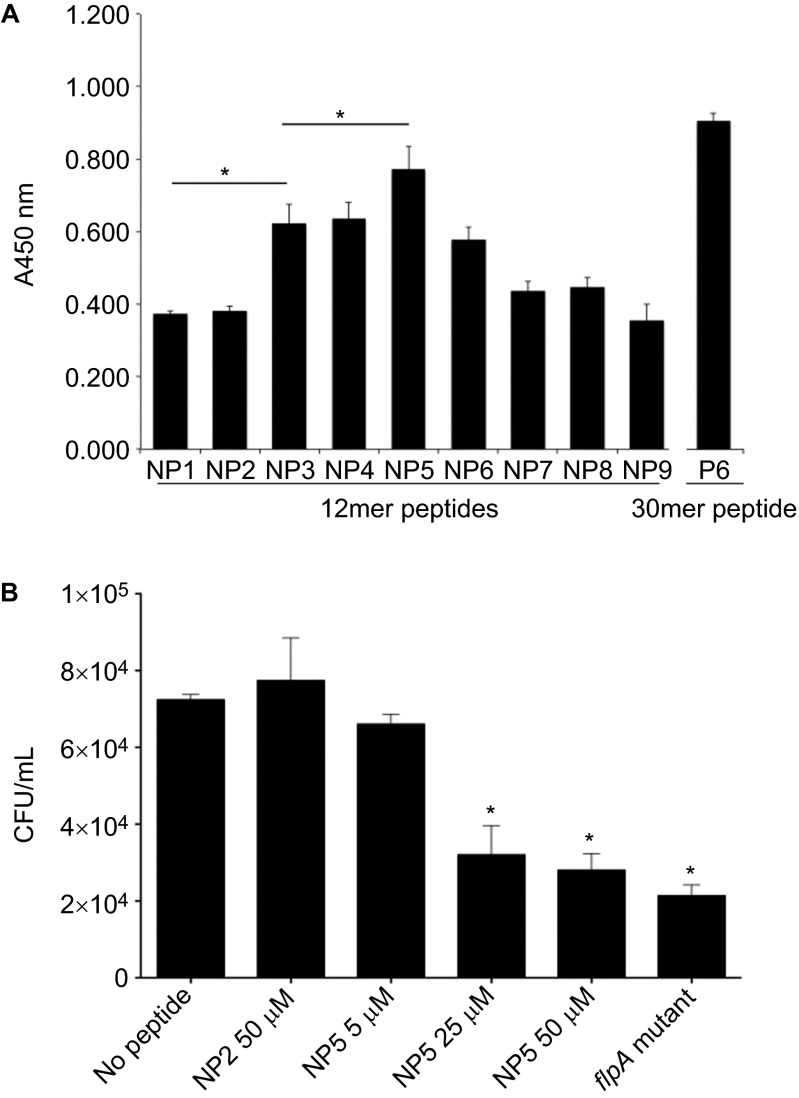
Figure 4.
The 12mer peptide NP5 competitively inhibits FlpA-mediated adherence of C. jejuni. (A) Binding of Fn to 96-well plates coated with peptides NP1–9. Ninety-six-well plates were coated with 12mer peptides (NP1–9) spanning the N150–V164 region of FlpA-D2. Fn was added to the peptide coated wells and the amount of Fn bound was measured by ELISA. The P6 30mer peptide used above was included as a positive control. Data are displayed as mean values and stan dard deviations from triplicate samples and statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA using Tukey's post-test (*P<0.05). (B) C. jejuni binding to wells coated with Fn pretreated with FlpA peptides. Ninety-six-well plates were coated with Fn and then blocked with peptides NP5 or NP2 at the indicated concentrations. A suspension of C. jejuni was added to the wells. After incubation and washing, the bacteria were collected by trypsinization and plated to determine CFU. The C. jejuni flpA mutant was also included as a negative control. Triplicate samples were used to calculate means and standard deviations plotted. The number of C. jejuni bound to the no peptide control wells was compared to the peptide treated samples and statistical difference was determined by one-way ANOVA using Tukey's post-test (*P<0.05).