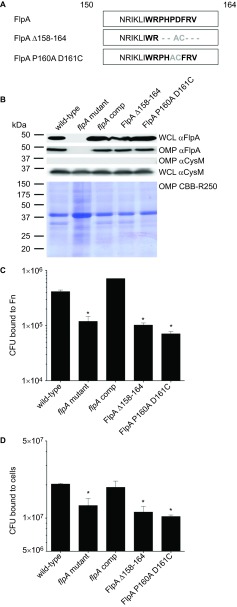
Figure 5.
Mutation of the FlpA FBLM abrogates FlpA-mediated adherence. (A) Sequence modifications for generation of FlpA Δ158–164 and FlpA P160A D161. Non-native residues (gray) result from enzyme restriction sites introduced for removal of the FBLM residues. (B) FlpA protein synthesis and outer membrane insertion. WCLs and OMP extracts from C. jejuni flpA mutant strains synthesizing FlpA, FlpA Δ158–164 and FlpA P160A D161C proteins were immunoblotted with FlpA-specific rabbit serum. OMP extracts were stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB-R250) to show equal loading. (C) Binding of C. jejuni flpA mutant strains synthesizing the FlpA, FlpA Δ158–164, and FlpA P160A D161C proteins to immobilized Fn. C. jejuni were added to 96-well plates coated with Fn and the CFU bound to each well were determined. C. jejuni wild-type and the flpA mutant were included as positive and negative controls, respectively. (D) Binding of C. jejuni flpA mutant strains synthesizing the FlpA, FlpA Δ158–164 and FlpA P160A D161C proteins to INT 407 epithelial cells. All C. jejuni binding experiments were performed three times with triplicate samples per experiment. The means and standard deviations are plotted and statistical difference was determined by ANOVA using Tukey's post-test (*P<0.05). CFU, colony-forming unit; OMP, outer membrane protein; WCL, whole-cell lysate.