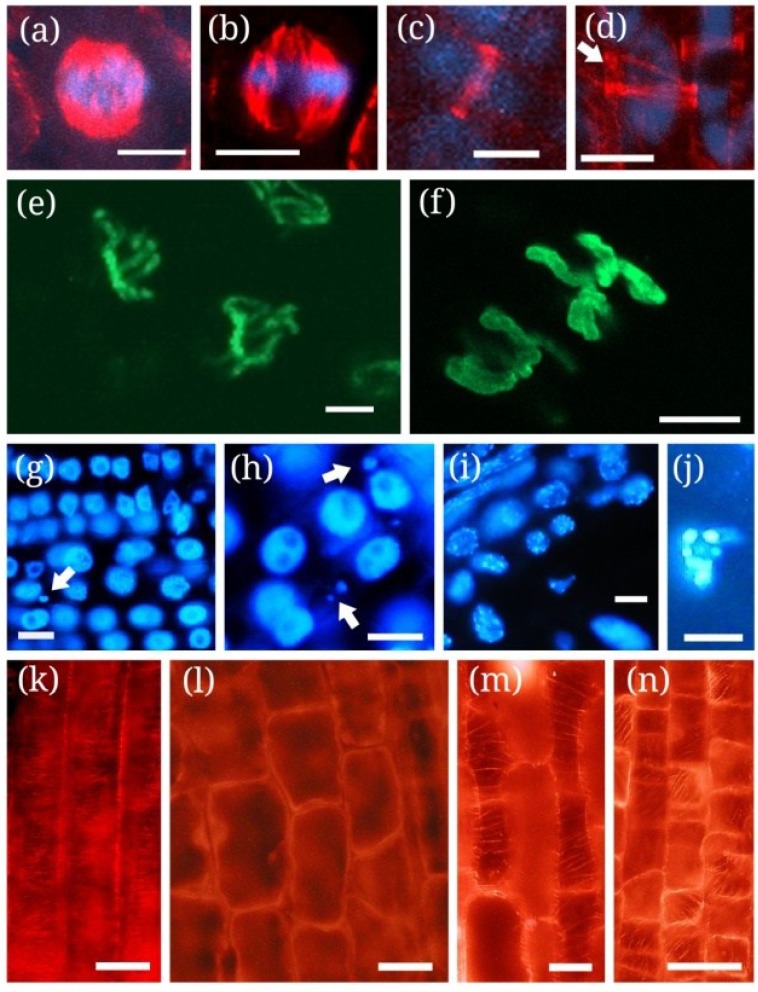
Figure 1.
Conventional fluorescence (g–n) and confocal microscopy (a–f) images of characteristic chromatin and microtubule alterations induced by cyanotoxins in plant cells as revealed by histochemical and immunohistochemical methods (see [105] as an example for methods). Chromatin label is shown in blue, Ser10-phosphorylated histone H3 in green and microtubules in red. (a) Normal metaphase spindle from in vitro cultured control Phragmites australis root tip meristem; (b) P. australis root tip meristem cell treated with 10 μg mL−1 MCY-LR. Note abnormal bundling of microtubules and spindle disruption; (c) Prophase cell of a P. australis root tip with normal preprophase band (PPB); (d) Split PPB (arrow) of a P. australis cell treated with 10 μg mL−1 CYN; (e) Control Vicia faba root tip meristem cell labeled for phospho-histone H3 Ser10. Histone H3 is phosphorylated mainly at the pericentromeric regions of metaphase chromosomes; (f) V. faba cell treated with 20 μg mL−1 MCY-LR. Note histone H3 hyperphosphorylation both at pericentromeric regions and chromosome arms; (g) Nuclei of V. faba meristematic cells labeled with DAPI. Micronuclei occur only sporadically (arrow); (h) Abundance of micronuclei in V. faba meristem treated with 20 μg mL−1 MCY-LR (arrows); (i) Nuclei of Sinapis alba cells from root elongation zone labeled with DAPI. No micronuclei or nucleus fragmentation can be detected; (j) Fragmented nucleus of a Sinapis alba cell from root elongation zone treated with 1 μg mL−1 MCY-LR; (k) Control P. australis cells from root elongation zone, with normally oriented cortical microtubules (CMTs); (l) P.australis root cells treated with 20 µg mL−1 MCY-LR showing CMT depolymerization and inhibition of cell elongation; (m,n) P.australis root cells treated with 10 μg mL−1 CYN, showing a cell with decrease of MT density (m) and a cell with CMT reorientation, inhibition of elongation and stimulation of radial expansion of cells at the transition of meristematic-elongation zone (n). Scalebars: 15 μm (a,b), 10 µm (c,d,g–j), 5 µm (e,f); 30 µm (k,l), 25 µm (m,n). Micrographs taken by D. Beyer (a,b,e,f), C. Máthé (g–n) and J. Roszik (c,d).