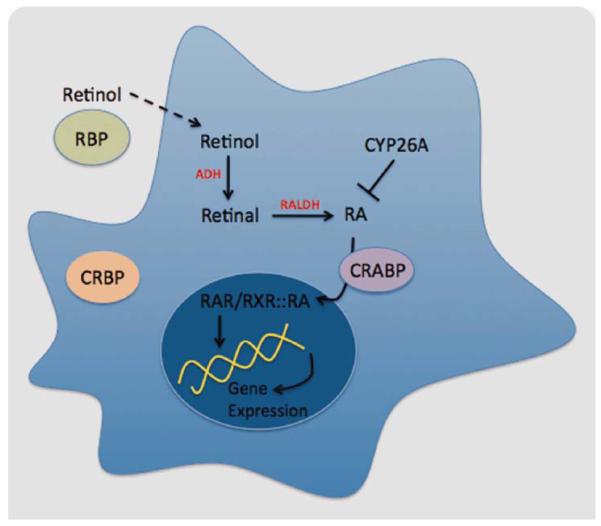
Fig. 1.
RA metabolism. Retinol gives rise to RA through the activity of different families of enzymes, including RALDH, which catalyzes the last step in an irreversible manner. Once in the cytoplasm, RA binds to CRABP and is transferred to the nucleus, where it is recognized by the nuclear receptors (RAR/RXR), and it binds to the DNA to regulate gene expression. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at wileyonlinelibrary.com.]