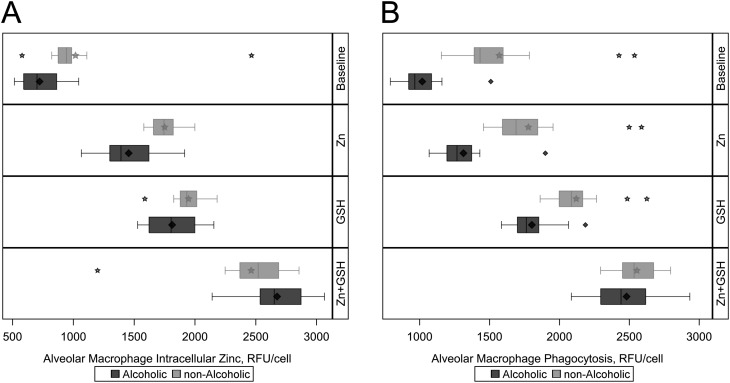
Figure 6.
Evaluation of intracellular zinc and phagocytic capacity in alveolar macrophages from alcoholic and nonalcoholic study participants after treatment ex vivo with zinc acetate (Zn; 10 μM), glutathione (GSH; 500 μM), or both zinc and GSH. Intracellular zinc and phagocytosis was measured as relative fluorescence units (RFU) per cell using confocal microscopy. (A) Median and interquartile ranges for post-treatment intracellular zinc among alcoholic and nonalcoholic subjects, with the baseline values displayed in the top bar. Intracellular zinc increases with zinc and GSH treatment alone, and combination treatment with both zinc and GSH results in intracellular zinc levels that are modestly higher in alcoholics (P = 0.0031). (B) Median and interquartile ranges for post-treatment phagocytosis among alcoholic and nonalcoholic subjects. Phagocytosis increases with zinc and GSH treatment alone, and combination treatment with both zinc and GSH also results in alveolar macrophage phagocytosis that is similar between alcoholics and nonalcoholics (P = 0.1188). The diamonds and stars represent mean values and outliers among alcoholics and nonalcoholics, respectively.