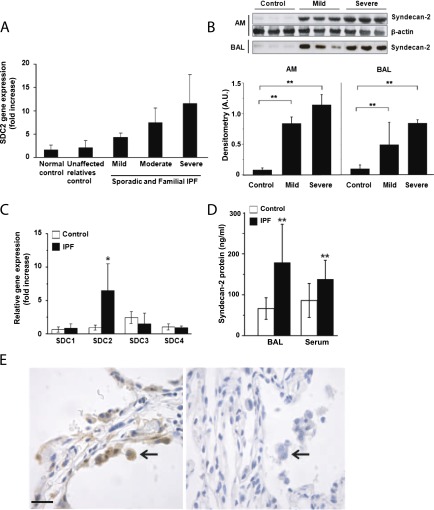
Figure 1.
Syndecan-2 up-regulation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). (A) Syndecan-2 (SDC2) gene expression by microarray analysis of alveolar macrophage (AM) mRNA in sporadic and familial IPF. (B) Syndecan-2 protein levels in AMs and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid were significantly increased in IPF compared with normal control subjects (n = 3 for each group; **P < 0.01). (C) Syndecan-2, and not syndecan-1, -3, or -4, gene expression by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction of alveolar macrophage mRNA was significantly increased in IPF (n = 5) compared with control subjects (n = 5) (*P < 0.05). (D) Syndecan-2 concentrations were significantly increased in BAL fluid and serum of subjects with (n = 38) compared with normal control subjects (n = 26) (**P < 0.01). (E) Syndecan-2 immunostaining of alveolar macrophages (arrows) was more intense in lung tissue sections from subjects with IPF (left panel) compared with those of control subjects (right panel). Scale bars = 20 μm.