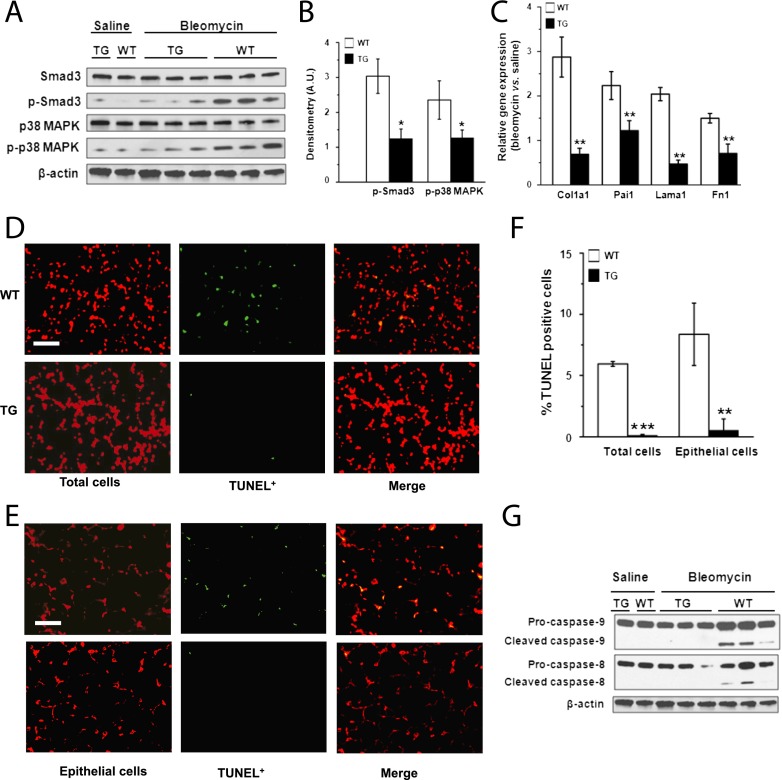
Figure 3.
Inhibition of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 signaling and lung apoptosis in scavenger receptor A enhancer/promoter (SREP)–human syndecan-2 (hsdc2) transgenic mice. (A) Representative Western blot analyses showed reductions in phosphorylated SMAD3 and p38 MAPK in lungs of SREP-hsdc2 transgenic (TG) mice compared with wild-type (WT) mice 21 days after administration of bleomycin and not saline. (B) Densitometry shows significant reduction of phosphorylated SMAD3 and p38 MAPK in lungs from TG mice compared with WT control mice (*P = 0.02 and *P = 0.04, respectively; n = 3). (C) Gene expression measured by quantitative polymerase chain reaction of Col1a1, Pai1, Lama1, and Fn1, which are TGF-β1 target genes, was significantly down-regulated in lungs of TG mice compared with WT control mice 21 days after bleomycin administration (**P < 0.01; n = 3). (D) Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) staining of lung tissue 21 days after intratracheal instillation of bleomycin showed less apoptosis in TG mice compared with WT mice. Total cells were counterstained with propidium iodide (red). TUNEL-positive cells appear green or yellow (in merged images) (scale bar = 25 μm). (E) Epithelial cells in lung tissue sections were counterstained with an antibody to cytokeratin (red). Fewer TUNEL-positive cells (green or yellow [in merged images]) were found in TG mice compared with WT control mice 21 days after administration of bleomycin (scale bar = 25 μm). (F) Apoptotic cell index was calculated as the number of TUNEL-positive cells per 100 total or epithelial cells. The apoptotic cell index of total or epithelial cells was significantly reduced in lung tissue from TG mice compared with WT mice (***P < 0.001; **P = 0.002). (G) Consistent with these findings of decreased apoptosis in TG mice, Western immunoblot analyses showed reduced levels of cleaved caspase-8 and -9 in lungs from TG mice compared with WT control mice.