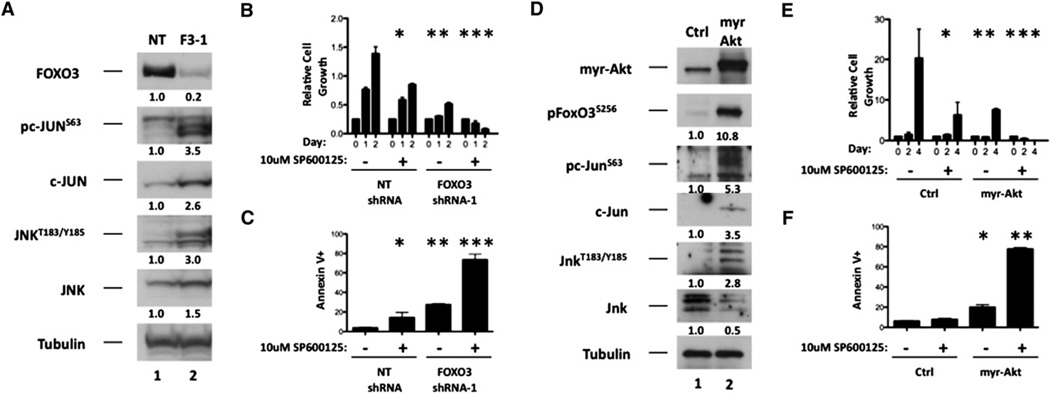
Figure 6. The JNK/c-JUN Signaling Pathway Antagonizes Maturation and Apoptosis Mediated by FOXO Inhibition in AML.
(A) MOLM-14 cells stably expressing either nontargeting (NT) or FOXO3 (FOXO3-1) shRNA were subjected to western blotting with antibodies that specifically recognize FOXO3, c-JUN, JNK, Tubulin, or the phosphorylated forms of c-JUN (pc-JUNS63) and JNK (pJNKT183/Y185).
(B and C) MOLM-14 cells stably expressing nontargeting (NT) or FOXO3 (F3-1) shRNA were treated with 10 µM SP600125 (JNK inhibitor) or vehicle. Forty-eight hours later, cells from each condition were assessed for cell number (B, NT [vehicle] versus NT [SP600125], *p = 0.0095, NT [SP600125] versus F3-1 [vehicle], **p = 0.0008, F3-1 [vehicle] versus F3-1 [SP600125], ***p < 0.0001) and Annexin V staining (C, NT [vehicle] versus NT [SP600125], *p = 0.0282, NT [SP600125] versus F3-1 [vehicle], **p = 0.0133, F3-1 [vehicle] versus F3-1 [SP600125], ***p = 0.0002). Data are represented as the mean ± SD.
(D) Control and myr-Akt-expressing MLL-AF9+ leukemia BM cells were subjected to western blotting with FoxO3, c-Jun, Jnk, Tubulin, or the phosphorylated forms of FoxO3 (pFoxO3S256), c-Jun (pc-JUNS63), and Jnk (pJnkT183/Y185) antibodies.
(E and F) Control and myr-Akt-expressing MLL-AF9+ leukemia BM cells were treated with 10 µM SP600125 (JNK inhibitor) or vehicle. Forty-eight hours after treatment, cells from each condition were assessed for cell number (E, Ctrl [vehicle] versus Ctrl [SP600125], *p = 0.0373, Ctrl [vehicle] versus myr-Akt [vehicle], **p=0.0381, myr-Akt [vehicle] versus myr-Akt [SP600125], ***p< 0.0001) and Annexin Vstaining (F, Ctrl [SP600125] versus myr-Akt [vehicle], *p =0.0011, myr-Akt [vehicle] versus myr-Akt [SP600125], **p < 0.0001). Data are represented as the mean ± SD.
See also Figure S6.