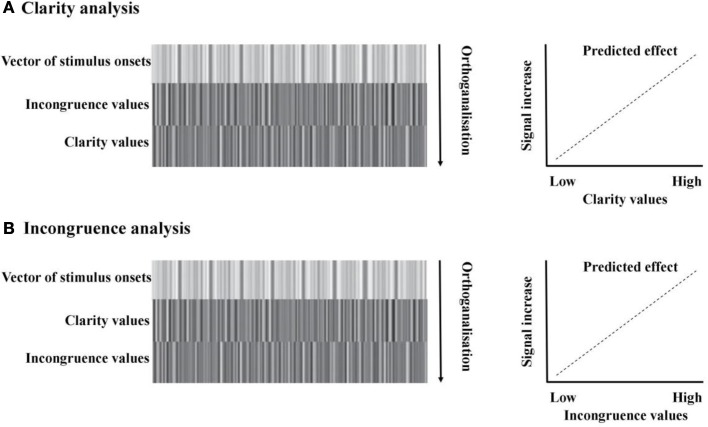
Figure 3.
fMRI analysis models. (A) Clarity analysis. The design matrix included one vector modeling all the onsets of the audiovisual stimuli, then two parametric modulators: the first modeling the incongruence value of each stimulus, and the second modeling the clarity value of each stimulus. Parametric modulators were serially orthogonalized, meaning that any variance associated with incongruence was removed. The linear expansion of the parametric modulator predicted that, with a positive loading on the modulator, as clarity values increased, there would be a related increase in signal. (B) Incongruence analysis. The design matrix included one vector modeling all the onsets of the audiovisual stimuli, then two parametric modulators: the first modeling the clarity value of each stimulus, and the second modeling the incongruence value of each stimulus. As previously, parametric modulators were serially orthogonalized, meaning that any variance associated with clarity was removed. The linear expansion of the parametric modulator predicted that, with a positive loading on the modulator, as incongruence values increased, there would be a related increase in signal.