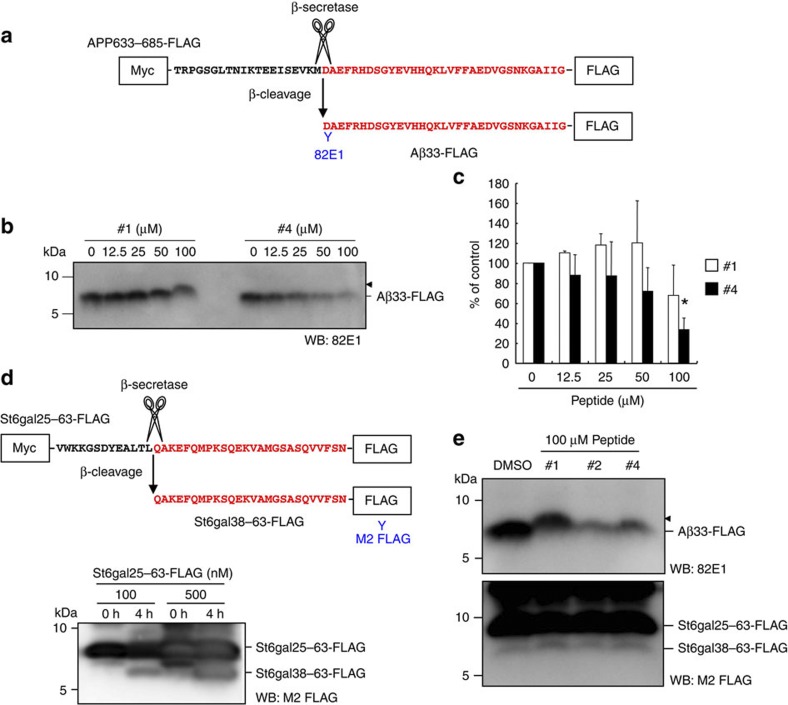
Figure 7. C99-binding peptides inhibited β-cleavage of APP in a substrate-specific manner.
A fragment of human APP751 (position 633–685) was expressed as a fusion protein with N-terminal Myc and C-terminal FLAG tags in E. coli BL21 and was affinity purified using Anti-FLAG M2 beads. Resultant APP633–685-FLAG was cleaved by β-secretase to produce Aβ33-FLAG (a). Peptide #4 significantly inhibited β-cleavage of the APP633–685-FLAG in a dose-dependent manner (b). The arrowhead indicates the retardation of Aβ33-FLAG migration caused by peptide #1. Data are expressed as means±s.d. of three independent experiments. *P<0.05 (analysis of variance (ANOVA), Scheffe’s post hoc test compared with DMSO control). A fragment of rat St6gal1 (position 25–63, St6gal25–63-FLAG) was incubated with β-secretase to produce St6gal38–63-FLAG (c). C99-binding peptides inhibited β-cleavage of the APP633–685-FLAG (upper panel), but failed to suppress cleavage of St6gal25–63-FLAG (lower panel) (d). The arrowhead indicates the shifted Aβ33-FLAG migration as a probable effect of #1 peptide binding.