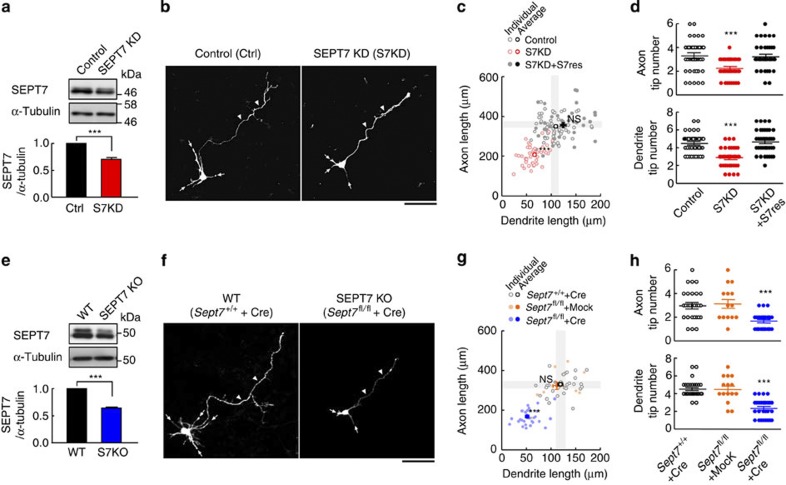
Figure 2. In vitro rescue and morphometry of the SEPT7-depletion phenotype on dendrite/axon growth.
(a) Immunoblot estimation of the gross efficiency (including GFP-negative untransfected population) of SEPT7 depletion from wild-type E17 embryo-derived neurons via S7KD#1 RNAi (div2). Each lane contained 10 μg protein. (Triplicated experiments. ***P<0.001 by t-test). Error bars denote s.e.m. (b) Representative images for the morphometry of GFP-positive pyramidal-like neurons with dendrites (arrows) and axons (arrowheads). Scale bar, 50 μm. (c) Scattergram of the total lengths of the axon and dendrites from each neuron expressing the designated plasmid(s). Dendrites and axons of SEPT7-depleted neurons (S7KD, red) were significantly and proportionally shorter than control neurons (black) whose average±2 s.e.m. is indicated as grey zones. The SEPT7-depletion phenotype was rescued by the co-expression of an RNAi-resistant mRNA encoding mCherry-SEPT7 (S7KD+S7res, closed circles). (n=45 × 3. ***P<0.001; NS, P>0.05 by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey). Error bars denote s.e.m. (d) Significant differences in the tip numbers of axons and dendrites between the experimental groups (n=45 × 3. ***P<0.001 by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey), which were rescued as noted above. Error bars denote s.e.m. (e) Experiment comparable with (a), but using Sept7fl/fl embryo and Myc-Cre plasmid. Immunoblot estimation of the gross efficiency (including the untransfected population) of SEPT7 depletion after gene disruption (div2). See legend in (a). Error bars denote s.e.m. (f) Representative images for the morphometry of GFP/Cre-positive, Sept7+/+/wild type (WT) and Sept7fl/fl (SEPT7KO) pyramidal-like neurons. See legend in (b). (g) Scattergram of the total lengths of the axon and dendrites from each neuron with designated genotype ±Cre expression. Dendrites and axons of Sept7fl/fl +Cre (SEPT7KO, blue circles) neurons were significantly and proportionally shorter than those of control Sept7fl/fl −Cre (orange circles) neurons and Sept7+/+ +Cre (open circles) neurons whose average±2s.e.m. is indicated as grey zones. Statistical analysis showed that acute Sept7 disruption significantly and proportionally shortened their dendrites and axons. (n=30, 15, 30. ***P<0.001 by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey). Note that the short dendrite/axon phenotype elicited by gene disruption was more severe than elicited by RNAi in (c). Error bars denote s.e.m. (h) The tip numbers of axons and dendrites were significantly reduced after Sept7 disruption. (n=30, 15, 30. ***P<0.001 by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey). Error bars denote s.e.m.