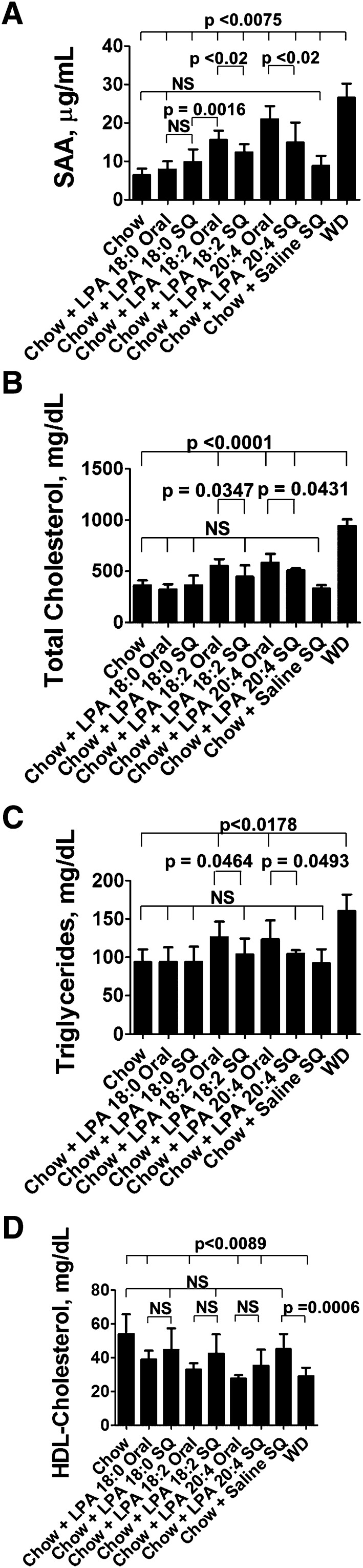
Fig. 11.
LPA administered orally to LDLR−/− mice is modestly but significantly more potent than the same dose administered by SQ injection. Female LDLR−/− mice, age 3 months (n = 8 per group), were fed mouse chow (Chow), WD, or chow supplemented with 4 μg of LPA (18:0, 18:2, or 20:4) per gram chow. Each night the mice were given 16 g of chow for each cage of four mice. The mice ate all of the diet each night. Other mice received mouse chow without LPA and received daily SQ injections on the back of 16 μg of LPA (18:0, 18:2, or 20:4) in saline, or they received saline alone. After 2 weeks, plasma levels of SAA (A), total cholesterol (B), plasma triglycerides (C), and plasma HDL-cholesterol (D) were determined as described in Materials and Methods. Data are mean ± SD.