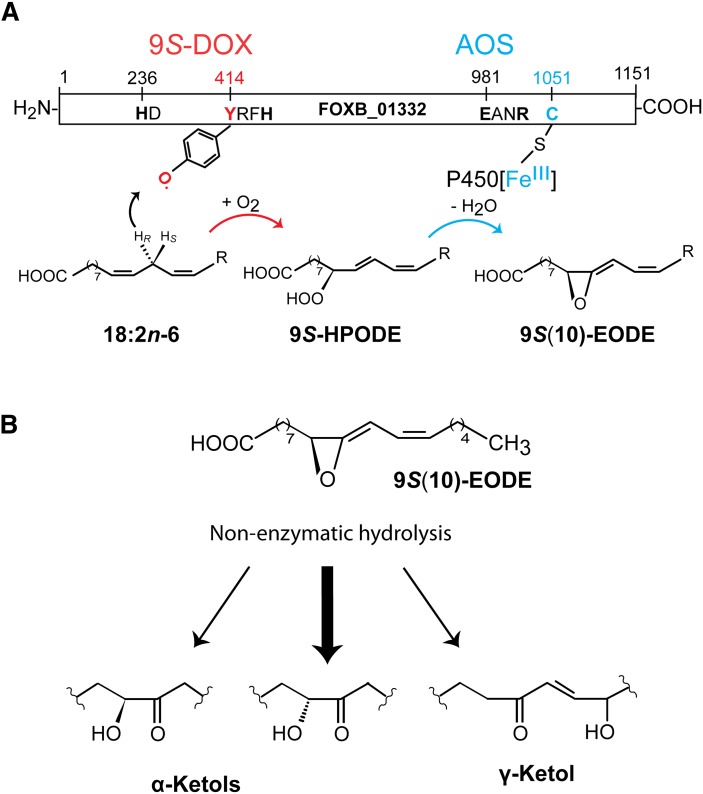
Fig. 8.
Overview of 9S-DOX-AOS domains, the biosynthesis of 9S-HPODE and 9S(10)-EODE from 18:2n-6, and the nonenzymatic hydrolysis of 9S(10)-EODE. A: Overview of the 9S-DOX and AOS domains. The former contains the distal heme ligand, His236 (marked HD) and the catalytic domain with Tyr414. The latter is likely oxidized to a tyrosyl radical, which abstracts the proR hydrogen at C-11 and molecular oxygen is inserted at C-9. The AOS domain contains the salt bridge (Glu981 and Arg984) and the heme thiolate ligand (Cys1051). CYP[FeIII] catalyzes homolytic scission of the oxygen bond with formation of CYP[FeIVOH]. The latter desaturates the 9(10)-epoxide intermediate with a radical at C-11 and forms the double bond between C-10 and C-11. B: Nonenzymatic hydrolysis of 9S(10)-EODE yields α-ketols and small amounts of γ-ketols. The relative amounts of the two α-ketols differ during nonenzymatic hydrolysis of 9S(10)-EODE due to steric hindrance at C-9.