Fig. 1.
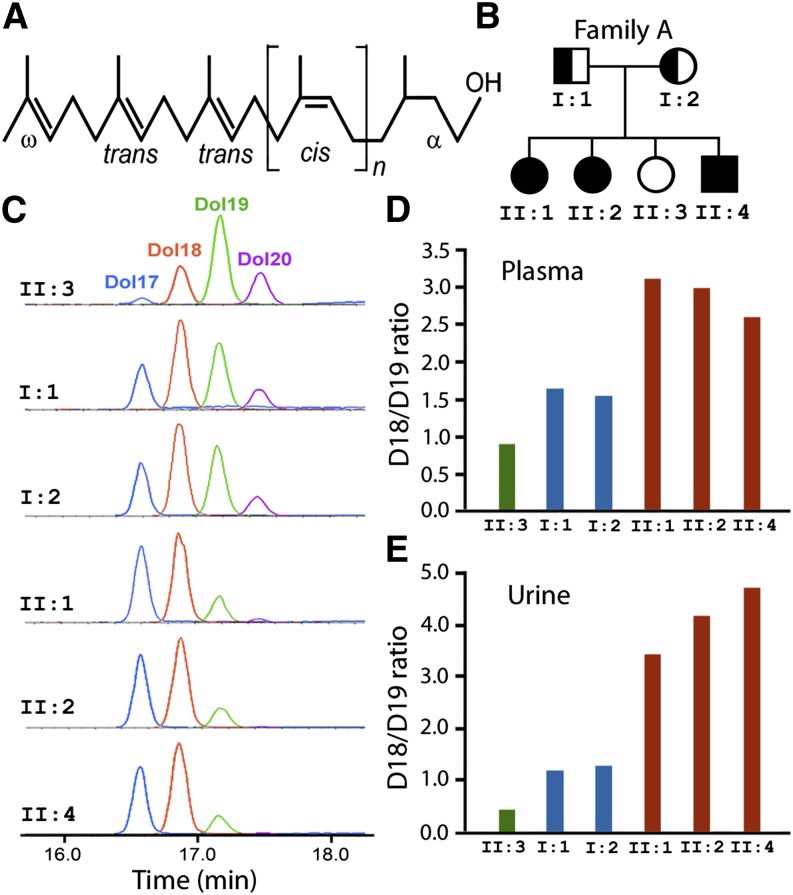
Plasma and urinary dolichol profiles of Family A. (A) Structure of dolichols. Dolichols are long-chain polyisoprenoid alcohols with a saturated α-isoprene unit and two trans units at the ω-end. (B) Pedigree of Family A. Three of the four siblings are homozygous for the K42E DHDDS mutation and were diagnosed with RP. (C) LC-MRM chromatograms of urinary dolichol profiles of all six family members. Dolichol profiles of those with K42E/K42E genotype are shortened, and D18 [II:1, II:2, and II:4 (orange)] becomes the dominant dolichol instead of D19 [II:3 (green)]. (D and E) The D18/D19 ratios of the affected individuals (red bars) are much higher than that of the unaffected individual (green bars), whereas the ratios of the K42E carriers (blue bars) are lower than those of the patients but higher than the unaffected individuals. The separation of D18/D19 ratios among affected siblings, parents (carriers), and the unaffected sibling is greater in urine than in plasma.