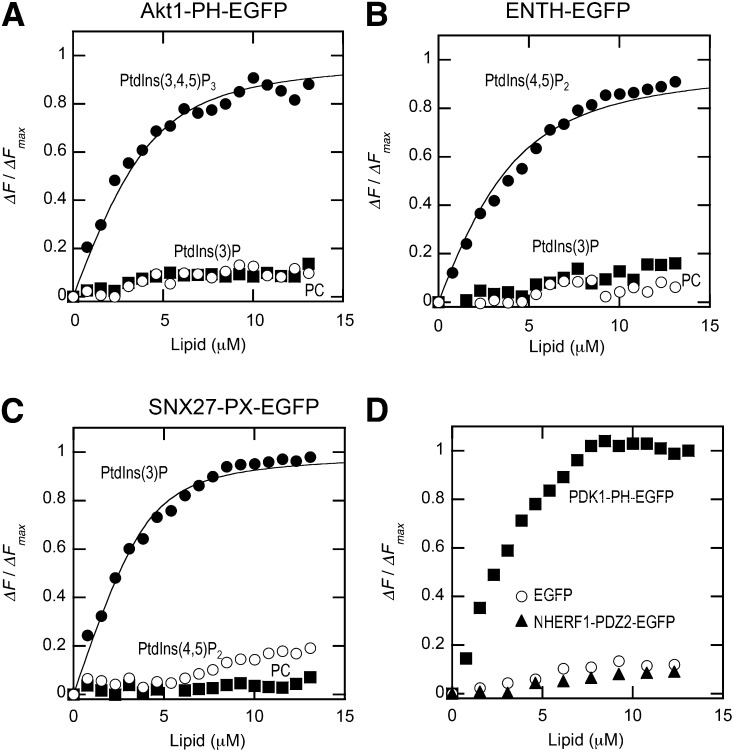
Fig. 4.
Binding isotherms of Akt1-PH-EGFP (A), ENTH-EGFP (B), SNX27-PX-EGFP (C), and EGFP and SNX5-PX-EGFP (D) (all 100 nM) with vesicles with various compositions measured in the cuvette-based assay. The binding isotherms for vesicles containing the most preferred lipid (e.g., POPC/POPS/dabsyl-PE/PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 (72:20:5:3) for Akt1-PH-EGFP) were fit by nonlinear least-squares analysis using equation 1. Values of n and Kd are summarized in Table 1. ΔF/ΔFmax was calculated as described for Fig. 3B. For binding of EGFP and NHERF1-PDZ2-EGFP to POPC/POPS/dabsyl-PE/PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 vesicles (D), binding of PDK1-PH-EGFP (100 nM) to the same vesicles was also shown to demonstrate the negligible membrane binding of these negative controls.