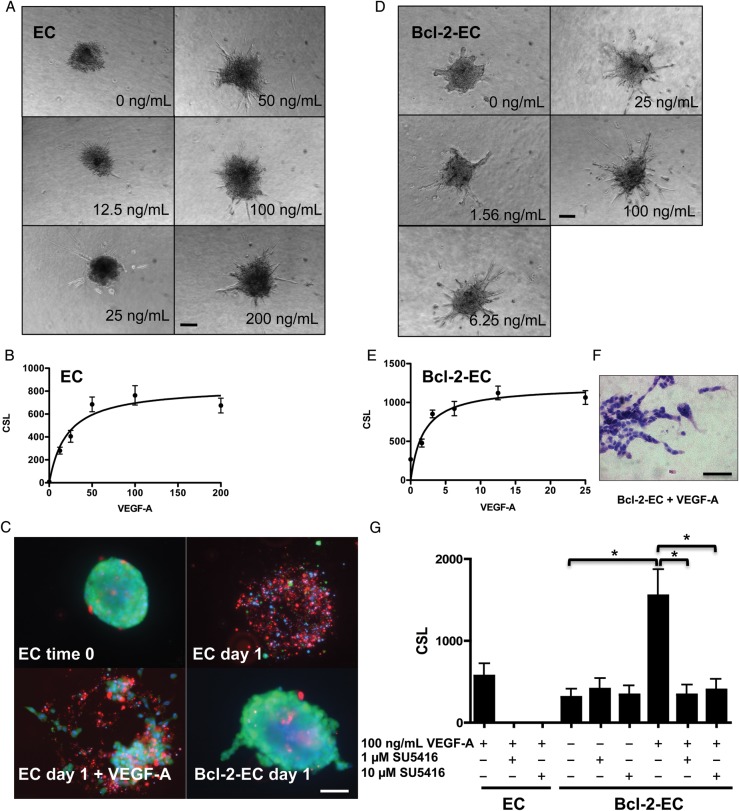
Figure 1.
Sprout formation by EC and Bcl-2-EC spheroids in response to VEGF-A. (A and D) Phase contrast micrographs of (A) EC and (D) Bcl-2-EC spheroids embedded in collagen gels containing increasing concentrations of VEGF-A (ng/mL). (B and E) Non-linear regression modelling and best fit of (B) EC and (E) Bcl-2-EC CSL ± standard error as a function of VEGF-A concentration. (C) Live/dead cell survival assays with non-transduced ECs spheres at time 0, after 1 day ± 100 ng/mL VEGF-A in collagen gels or Bcl-2-EC spheroids after 1 day without VEGF-A. Live cells fluoresce (green), dead or damaged cell nuclei (red), and both live and dead nuclei (blue). (F) H&E of Bcl-2-EC spheroids after 1 day with 100 ng/mL VEGF-A. (G) The effect of VEGF inhibitor SU5416 on sprouting by EC and Bcl-2-EC spheroids. Scale bars are 100 µm (A, D, and F) and 60 µm (C). The asterisk indicates statistically significant difference by a two-tailed t-test with post hoc Bonferroni correction (P < 0.017).