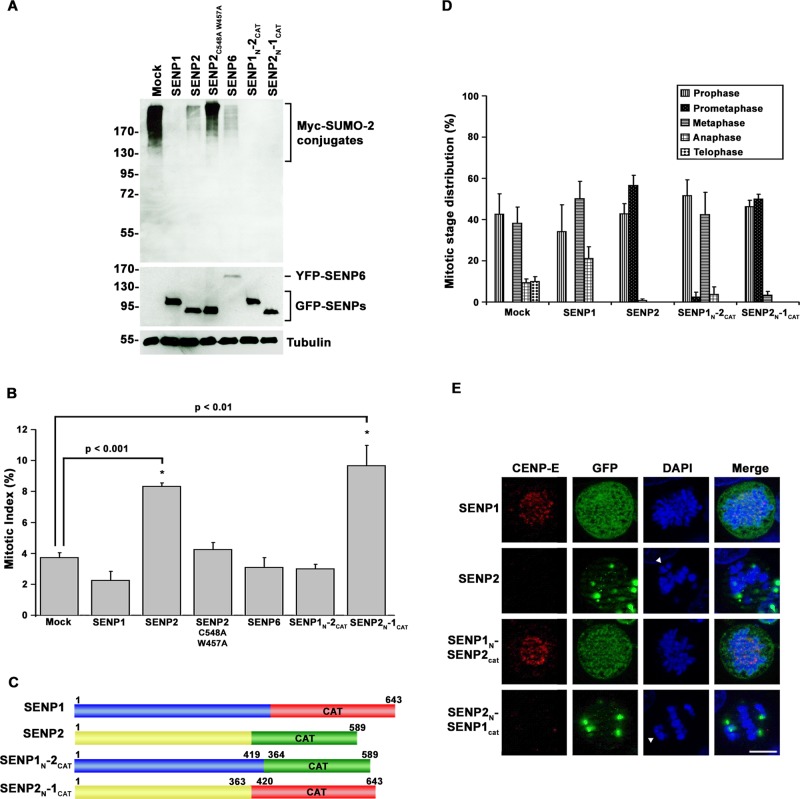
FIGURE 1:
SENP2 overexpression uniquely affects mitotic progression through mechanisms dependent on its N-terminal domain. (A) HeLa cells were cotransfected with constructs coding for Myc-tagged SUMO-2 and the indicated GFP-tagged SUMO isopeptidases or empty vector (Mock) as control. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblot analysis with antibodies specific for Myc, GFP, or tubulin. (B) HeLa cells were transfected with constructs coding for the indicated GFP-tagged SUMO isopeptidases or empty vector (Mock). The fraction of transfected cells in mitosis was determined by fluorescence microscopy 48 h after transfection. (C) Schematic diagram of SENP1, SENP2, and SENP1/2 chimeras. CAT, catalytic domain. (D) HeLa cells were transfected with constructs coding for the indicated SUMO isopeptidases or empty vector (Mock). The fraction of transfected cells present at each of the indicated stages of mitosis was determined by fluorescence microscopy 48 h after transfection. (E) HeLa cells were transfected with constructs coding for SENP1, SENP2, or the indicated chimeras. Cells were stained with CENP-E–specific antibodies and analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy. DNA was stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Arrowheads indicate unaligned chromosome pairs. Bar, 10 μm. Error bars represent SDs from three independent experiments.