Figure 1.
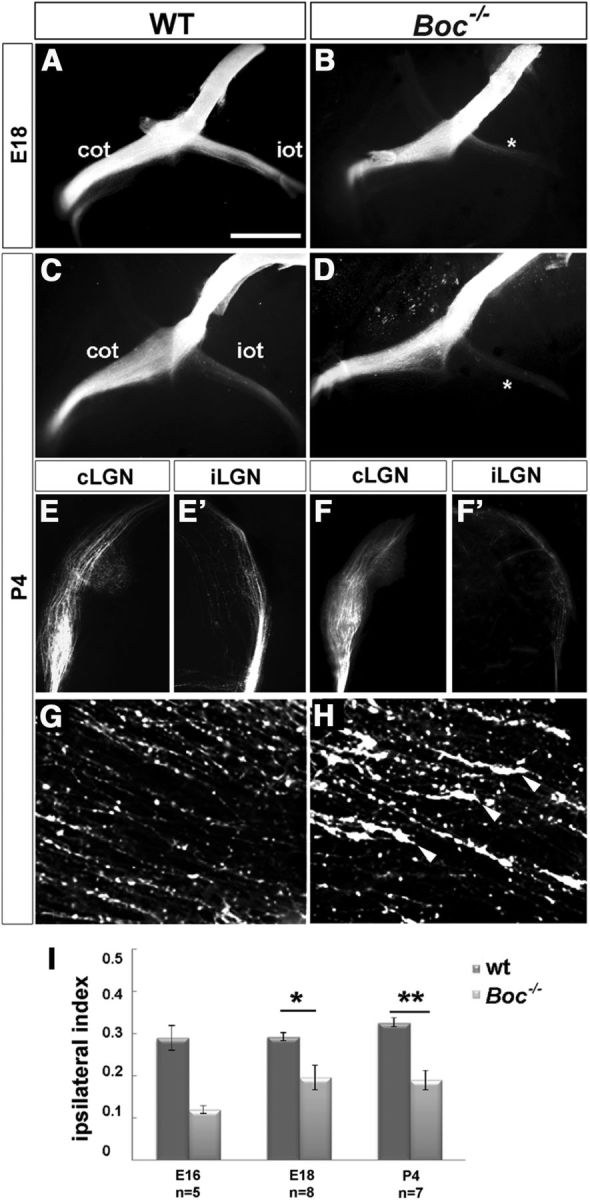
Boc−/− mice present a reduction of uncrossed retinal projections. A–H, Ventral views of the intact brains (A–D) and frontal (E–F′) or horizontal (G,H) vibratome sections through the contralateral and ipsilateral dLGN (E–F′) and optic chiasm (G,H) from E18 and P4 WT and Boc−/− animals (as indicated in the panels) with unilateral DiI filling of the optic disk to visualize visual fiber trajectory. There is strong reduction of projecting fibers in the ipsilateral lateral geniculate nucleus (iLGN) of the mutants. *Ipsilateral reduction. F, Arrowheads indicate growth cones in the initial portion of the mutant ipsilateral optic tract. I, The graph compares the values of the ipsilateral index in WT and Boc−/− mice at embryonic and postnatal stages. The number of analyzed animals is indicated in the graph for each stage. *p < 0.05 (Student's unpaired t test). **p < 0.01 (Student's unpaired t test). cLGN, Contralateral lateral geniculate nucleus; cot, contralateral optic chiasm; iot, ipsilateral optic tract. Scale bars: A–D, 1000 μm; E, F, 500 μm.
