Figure 7.
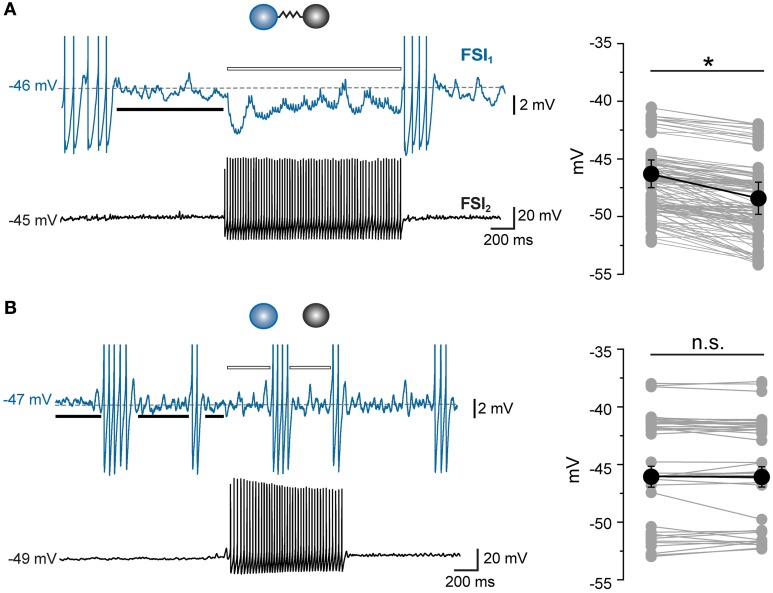
Gap junctions prevent postsynaptic firing by inducing Vm hyperpolarization at near-threshold levels. (A) Example of a GJ-only connected pair in which FSI1 displayed an array of subthreshold spikelets in response to a train of AP occurring in FSI2 during DC injection in both cells (380 and 405 pA, respectively, 20 s). The average Vm value of FSI1 during the spikelet barrage was measured throughout the duration of FSI2 burst (indicated by the white bar) and compared to the average Vm value before the burst onset (black bar). Right, summary of average Vm values measured in FSI1 before (left column) and during (right column) barrages of 4–8 spikelets occurring in response to AP burst in FSI2. Mean Vm ± s.e.m. values were significantly different in the two conditions (n = 22 pairs, *p < 0.05, paired t-test). (B) Same experiment as in (A), but with non-connected FSIs. Mean Vm ± s.e.m. in FSI1 did not change significantly during a burst in FSI2 (n = 10 pairs, p > 0.05, paired t-test). Transient changes in Vm corresponding to AP firing were excluded from measurements.