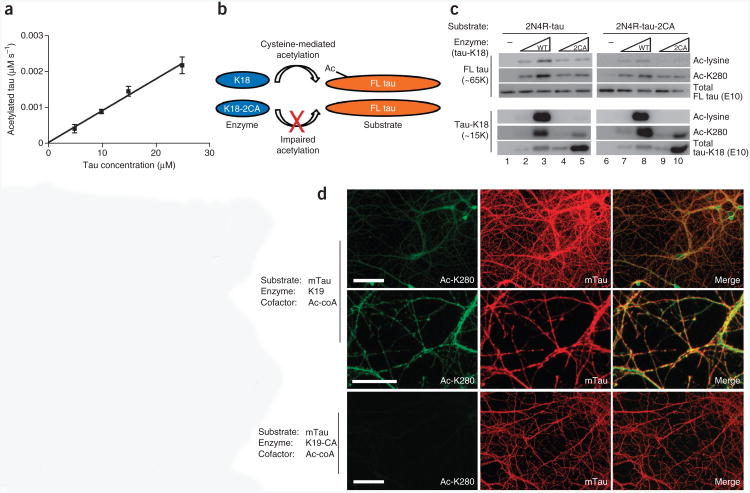
Figure 6.
Tau autoacetylation occurs by intra- and intermolecular mechanisms. (a) Plot of initial rate of autoacetylation versus tau-K18 concentration, for a 30-min reaction. Error bars, s.e.m. from n = 3 independent experiments. (Additional data are in Supplementary Fig. 4.) (b) Schematic of tau-K18-mediated acetylation of full-length 2N4R-tau, showing impaired acetyltransferase activity of the K18-2CA mutant toward full-length (FL) tau substrates. (c) Immunoblot analysis of 2N4R-tau and 2N4R-tau-2CA incubated with increasing concentrations of tau-K18 or tau-K18-2CA. Intermolecular tau acetylation products for full-length 2N4R-tau and tau-K18, analyzed with the indicated antibodies to tau, are shown. (d) Double-labeling immunofluorescence using antibodies to Ac-K280 or total mouse tau (mTau), assessing the ability of exogenously added 3R-tau to acetylate endogenous 4R-tau present in mature mouse neurons. Transacetylation immunofluorescence was performed by incubating purified tau-K19 (top and middle) or tau-K19-C322A mutant (bottom) with fixed and permeabilized hippocampal neurons. Immunofluorescence images are shown in low magnification (top and bottom; scale bars, 100 μm) and high magnification (middle; scale bar, 25 μm).