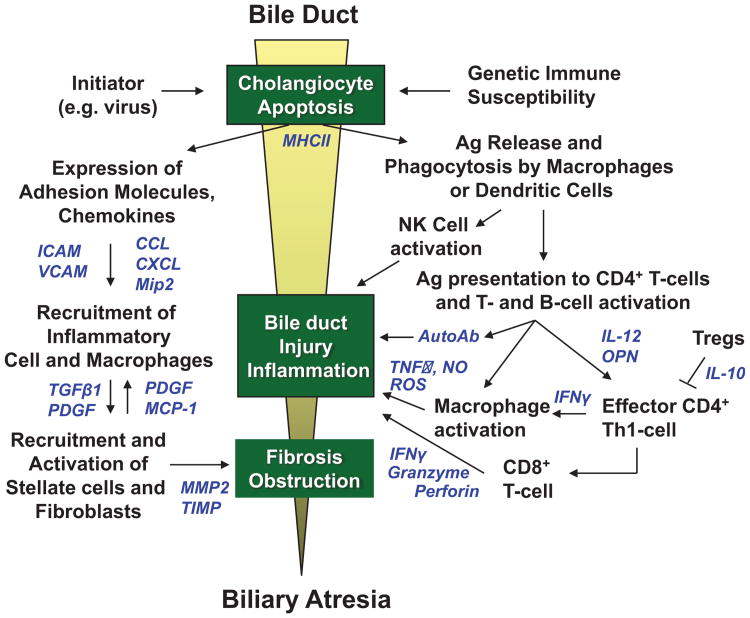
Figure 1.
Proposed etiology of bile duct injury in perinatal/acquired biliary atresia. A pre- or perinatal initiating event, such as a viral infection (rotavirus, reovirus, cytomegalovirus [CMV]) induces apoptosis of bile duct epithelia and aberrant MHC class II expression in extrahepatic and intrahepatic bile ducts in a genetically susceptible host. Viral, native, or altered bile duct antigens are phagocytosed by macrophages or dendritic cells and presented to naïve T cells in local lymph nodes in which CD4+ T cells are activated and proliferate (right side of figure). These activated CD4+ T cells (which may be autoreactive) home back to the original site of antigen exposure and elicit IFN-γ-induced macrophage stimulation and activation of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells and B cells. Release of TNF-α, nitric oxide (NO) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) by macrophages, autoantibodies by plasma cells, and granzyme, perforin, and interferon-γ (IFN-γ) by CD8+ T cells produce further cholangiocyte injury through apoptotic or necrotic pathways. Simultaneously, cholangiocytes and vascular endothelial cells upregulate expression of adhesion molecules and secrete chemokines to recruit neutrophils and macrophages to the site of bile duct injury (left side of figure). These cells then recruit and activate hepatic stellate cells (myofibroblasts) and fibroblasts, which secrete extracellular matrix causing fibrosis of injured bile ducts. The resulting cholangiocyte injury, inflammation, and fibrosis lead to complete bile duct obstruction and the phenotype of biliary atresia. Soluble inflammatory mediators in these pathways are shown in blue.