Fig. 2.
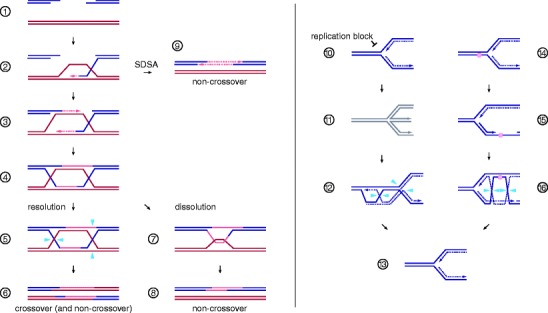
DNA double-strand break repair and replication fork support mediated by homologous recombination. Steps 1–6 describe the canonical DSB repair model of HR. 1, DNA end resection produces 3′-single-stranded overhangs which are bound by strand exchange protein Rad51/RAD51; 2, the resulting nucleoprotein-filament is capable of identifying and invading a homologous donor duplex, thereby creating a displacement-loop (D-loop) and initiating repair synthesis; 3, second-end capture, the association of the D-loop with the non-invading break end, also initiates repair synthesis; 4, after repair and nick ligation, the recombining molecules are joined together at a double HJ intermediate; 5, HJ resolvases introduce symmetrically related nicks (blue arrowheads) to produce discrete duplex products; 6, resolution of a pair of HJs along the same axis produces non-crossover products, while the use of different axes leads to crossover products characterized by reciprocal genetic exchange of flanking markers (as shown). Double HJ dissolution offers an alternative to nucleolytic cleavage: 7, the Sgs1–Top3–Rmi1/BLM–TOPOIIIα–RMI1–RMI2 complex drives HJ convergence by branch migration and removal of the resulting hemi-catenate; 8, dissolution results exclusively in non-crossover products, which differ from the DNA molecules at outset only by the presence of a repair patch. 9, Synthesis-dependent strand annealing (SDSA). Disassembly of the D-loop by expulsion of the invading DNA single-strand frees up a repair template for the second break end. 10–16, HR facilitates DNA replication: 10, a range of replication blocks may stall RF progression (see text); 11, a blocked RF (gray) can regress to form a HJ-like structure with a recombinogenic DSB end homologous to the DNA ahead of the four-way DNA junction; 12, HR-mediated strand-invasion forms a D-loop at which DNA synthesis may be re-initiated. HJs that arise during the process can be removed by nucleolytic cleavage (blue arrowheads) to reestablish a processive RF (13). 14, A lesion in the lagging strand template (pink sphere) can be bypassed without RF arrest; 15, the lesion is tolerated at the cost of a single-stranded DNA gap known as daughter strand gap; 16, HR-mediated gap repair and HJ formation. HJ resolution (blue arrowheads) or dissolution can restore a normal RF (13)
