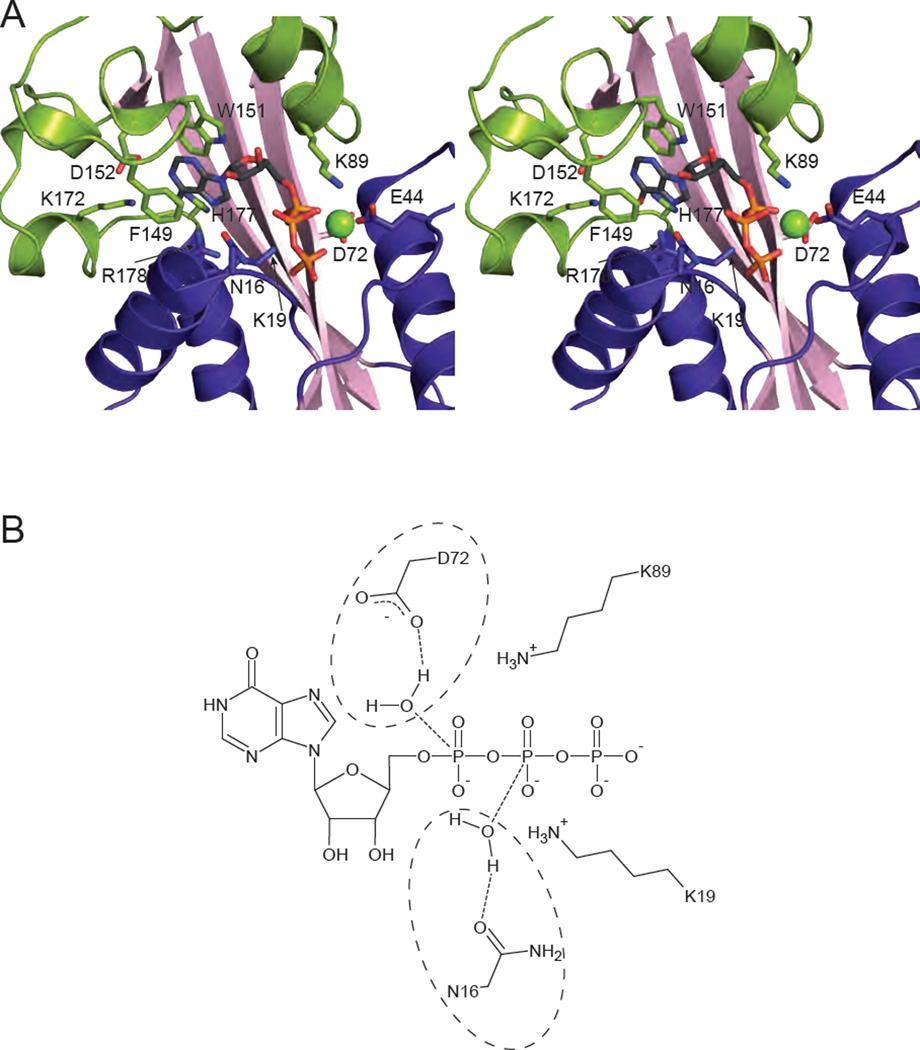
Fig. 2.
Substrate binding and catalysis. (A) Stereopair of ITPA with ITP bound (PDB code 2J4E [17]) is shown with relevant residues involved in substrate binding and discrimination shown in stick form. A Mg2+ cation is shown as a green sphere. (B) Potential reaction mechanisms for ITPA are shown schematically. Due to the low resolution of the structure, a single catalytic mechanism cannot be determined. Asp 72 is in position to coordinate a water molecule for attack on the α phosphate (circled on the top), while Asn-16 is positioned to coordinate a water for attack on the β phosphate (circled on the bottom). Either would result in the scission of the α-β phosphoanhydride bond. The positively charged ε-amino groups of Lys 19 and Lys 89 are positioned to stabilize the negatively charged intermediate.