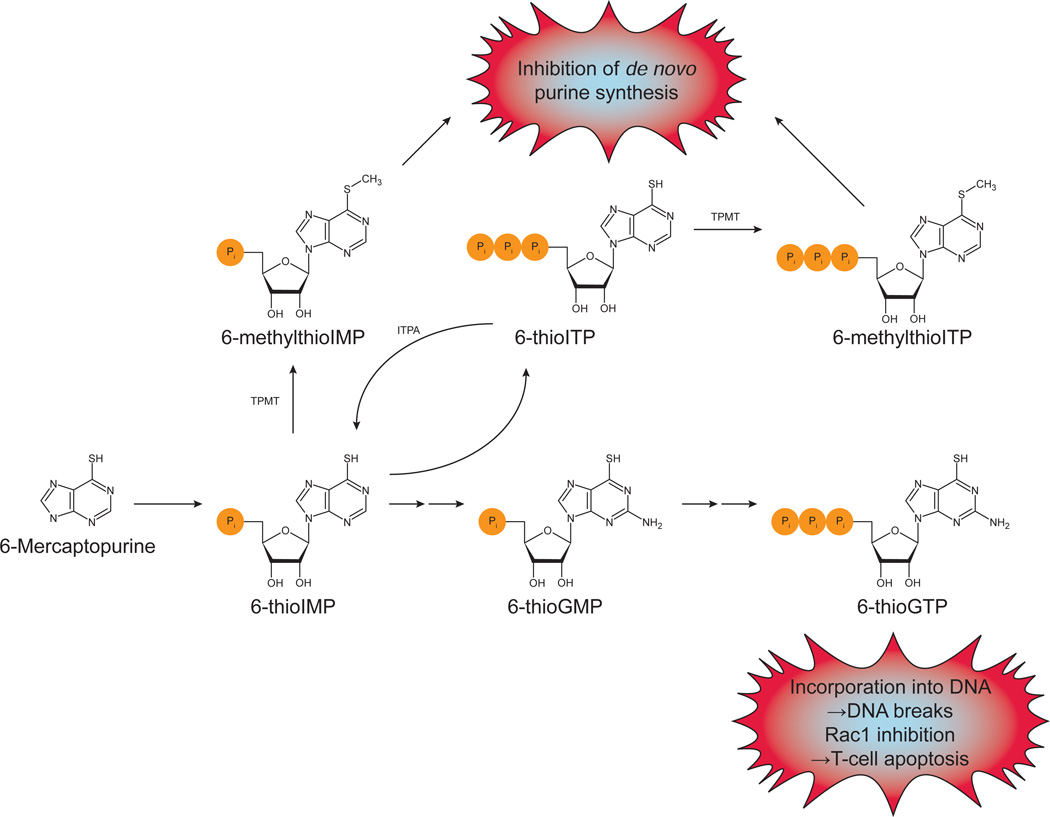
Fig. 7.
Mercaptopurine metabolism and mechanisms of cytotoxicity. After being taken up into cells, 6-mercaptopurine is converted to 6-thioIMP. (Azathioprine is a prodrug of 6-mercaptopurine.) 6-thioIMP can be converted to 6-thioGMP, which can be phosphorylated to 6-thioGTP. 6-thioGTP is known to cause DNA strand breaks by being incorporated into DNA and to induce T-cell apoptosis by Rac1 inhibition. 6-thioIMP can also be phosphorylated to 6-thioITP. ITPA can catalyze the conversion of this back to 6-thioIMP. TPMT can methylate both 6-thioIMP and 6-thioITP. These methylated forms inhibit de novo purine synthesis. In ITPA deficient patients, 6-thioITP and 6-methylthioITP can accumulate and lead to adverse reactions. Based on [108, 116, 117].