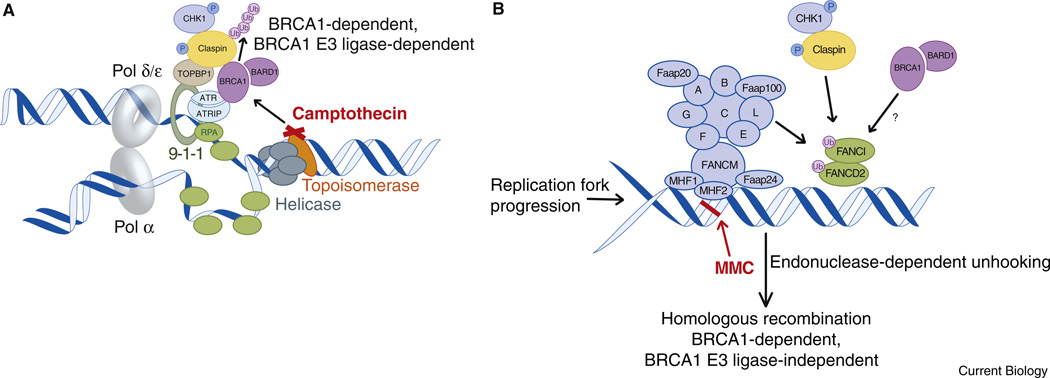
Figure 1. Differential DNA damage responses to Camptothecin and Mitomycin C treatment during replication.
(A) Topoisomerase poisons such as camptothecin induce replication-associated DNA double strand breaks and trigger a DNA damage response, which includes BRCA1-dependent ubiquitination of Claspin and activation of CHK1. (B) Forms of DNA damage involving inter-strand crosslinks are recognized by several Fanconi Anemia proteins, culminating in the monoubiquitination of the FANCD2/FANCI complex. Endo-nuclease processing of crosslinks is a prerequisite for subsequent repair of the lesion by homologous recombination. Claspin and BRCA1 also participate in promoting FANCD2 activation and BRCA1 is required for the later steps of homologous recombination after DNA double strand break formation.