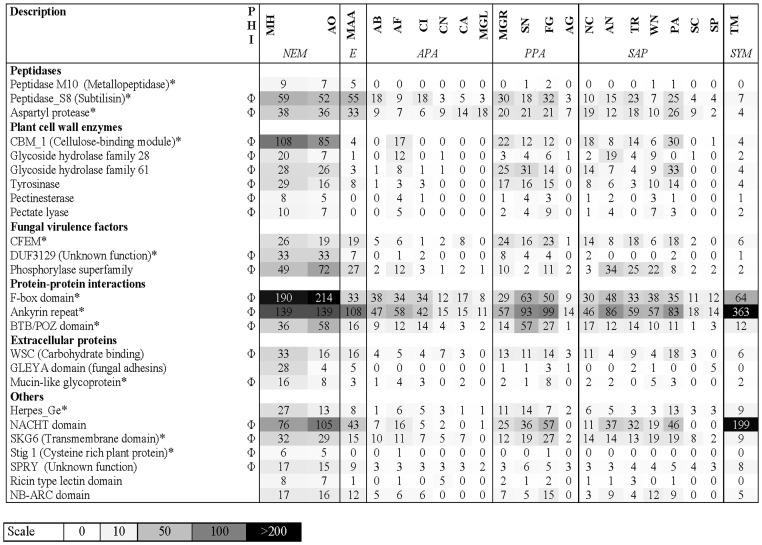
Figure 4. Expanded gene families in M. haptotylum.
The number of proteins in 25 Pfam families that were found to be significantly (P<0.001) enriched in the genome of M. haptotylum are compared with their sizes in 20 other fungal genomes. The symbol ‘*’ indicates that the family were also found among the lineage-specific families (Figure 2B). The symbol ‘Φ’ indicates that the Pfam family contains M. haptotylum proteins that match proteins (BLASTP, threshold value <1E -10) in the pathogen–host interaction (PHI-base) database [29]. Species and group abbreviations: NEM, the nematode-trapping fungi M. haptotylum (MH) and Arthrobotrys oligospora (AO); E, the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae (MAA); APA, animal pathogenic fungi including Arthroderma benhamiae (AB), Aspergillus fumigatus (AF), Coccidioides immitis (CI), Cryptococcus neoformans var neoformans (CN), Candida albicans (CA) and Malassezia globosa (MGL); PPA, plant pathogenic fungi including Magnaporthe oryzae (formerly M. grisea) (MGR), Stagonospora nodorum (SN), Fusarium graminearum (FG) and Ashbya gossypii (AG); SAP, the saprotrophic fungi including Neurospora crassa (NC), Aspergillus niger (AN), Trichoderma reesei (TR), Emericella nidulans (WN), Podospora anserina (PA), Saccharomyces cerevisiae (SC) and Schizosaccharomyces pombe (SP); SYM, the symbiotic fungus Tuber melanosporum (TM).