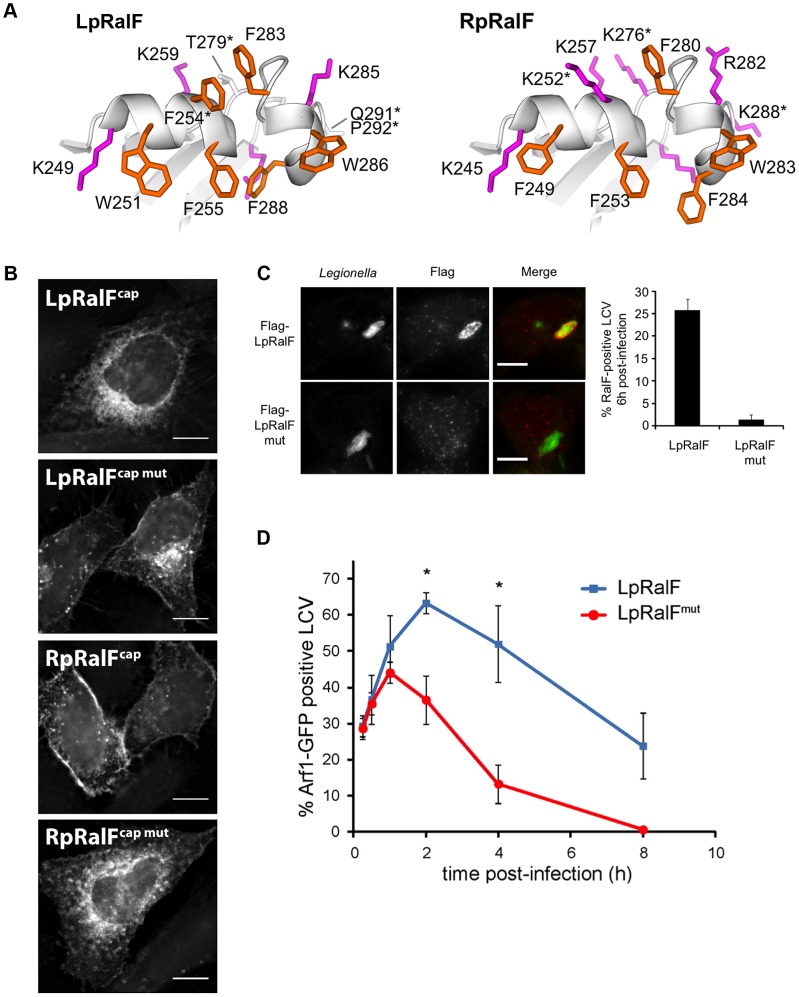
Figure 4. The aromatic cluster determines the capping domain localization to specific intracellular membranes. A. The aromatic clusters of LpRalF (left) and RpRalF (right) have a different ratio of aromatic (orange) and positively charged (magenta) residues.
RpRalF was modeled from the crystal structure of LpRalF (PDB entry 1XSZ, [13]). Residues mutated in the following experiments are indicated by an asterisk. B. The aromatic cluster determines LpRalF and RpRalF capping domain localization. HeLa cells expressing the indicated YFP-tagged RalF constructs were examined by fluorescence microscopy. Bar = 10 µm. C. Mutations in the aromatic cluster alter the residence time of LpRalF at the LCV. HEK293 cells were infected with L. pneumophila ΔralF complemented with a plasmid encoding either 3*Flag-LpRalF or 3*Flag-LpRalFmut. 6 h post-infection, cells were fixed and stained with anti-Flag antibodies (red). Legionella were stained with anti-Legionella antibodies (green). Bar = 10 µm. Quantification of RalF-positive vacuoles is shown. Represented is the average ± SEM (standard error of the mean) of 3 experiments where 50 vacuoles were counted. D. Mutations in the aromatic cluster of LpRalF alter the kinetics of Arf1 recruitment at the LCV. HEK293 cells stably expressing Arf1-GFP were infected with L. pneumophila ΔralF complemented with a plasmid encoding either 3*Flag-LpRalF or 3*Flag-LpRalFmut. Arf1-GFP recruitment to the LCV was quantified at different time points post-infection. RalF and RalFmut were expressed, translocated and present in the host cell 6 hours post-infection at the same level. Represented is the average ± SEM of 3 experiments where 50 vacuoles per time point were counted. (* P<0.05).