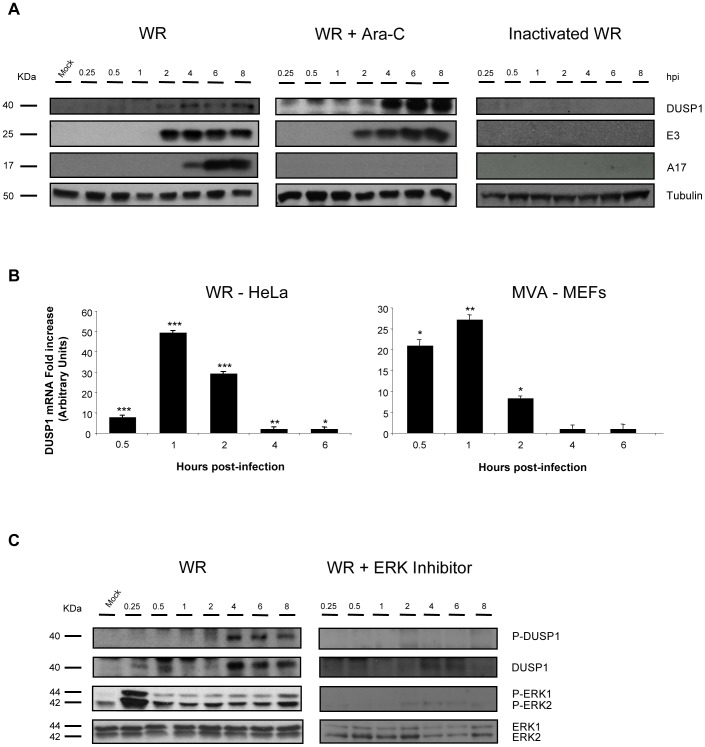
Figure 2. DUSP1 induction and phosphorylation requires early VACV gene expression and ERK activation.
A) DUSP1 protein levels after WR infection. HeLa cells with were treated with Ara-C (40 µg/ml) or left untreated and then subsequently mock-infected, infected with UV-inactivated WR or infected with WR at 5 PFU/cell. Equal amounts of proteins were analyzed by Western-blot using specific antibodies against DUSP1 or tubulin or viral proteins such as E3, A4 and A17. Lower graph represents fold increase of DUSP1 mRNA of CHX-treated WR-infected HeLa cells versus untreated WR-infected cells. mRNA levels are represented in Arbitrary Units. B) DUSP1 mRNA levels after VACV infection. HeLa cells or DUSP1 WT MEFs were treated with CHX (100 µg/ml) or left untreated and then subsequently infected at 5 PFU/cell with WR or MVA, respectively. Graphs represent fold increase of DUSP1 mRNA of CHX-treated infected cells versus untreated infected cells. mRNA levels determined by qRT-PCR are represented in Arbitrary Units. C) DUSP1 phosphorylation after WR infection. HeLa cells were treated with ERK inhibitor UO126 (50 µM/8 h) or left untreated and the infected as in A). Cells extracts were analyzed by Western-blot using antibodies against DUSP1, P-DUSP1, ERK, P-ERK or tubulin. p<0.05 (*), p<0.005 (**) and p<0.001 (***).