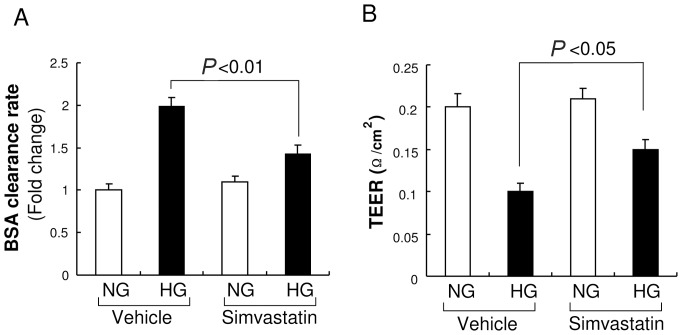
Figure 2. High glucose increases permeability of glomerular endothelial cells (GEnCs) and this effect is inhibited by simvastatin.
A: GEnC permeability was determined by measuring the amount of FITC-albumin that crossed the GEnCs monolayer during first hour after FITC-albumin (2 mg/mL) was added. High glucose (HG) increased permeability in GEnCs, as indicated by the rate of BSA transfer across the GEnCs monolayer, and simvastatin reduced this effect (n = 7). Data are presented as means ± SEMs. B: GEnC permeability was measured by transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER). HG reduced the TEER of the GEnC monolayer and simvastatin inhibited this response (n = 7). Data are presented as means ± SEMs.