Figure 1. Localization of octopamine receptors, tachykinin, and tachykinin receptors in the antennae of P. americana.
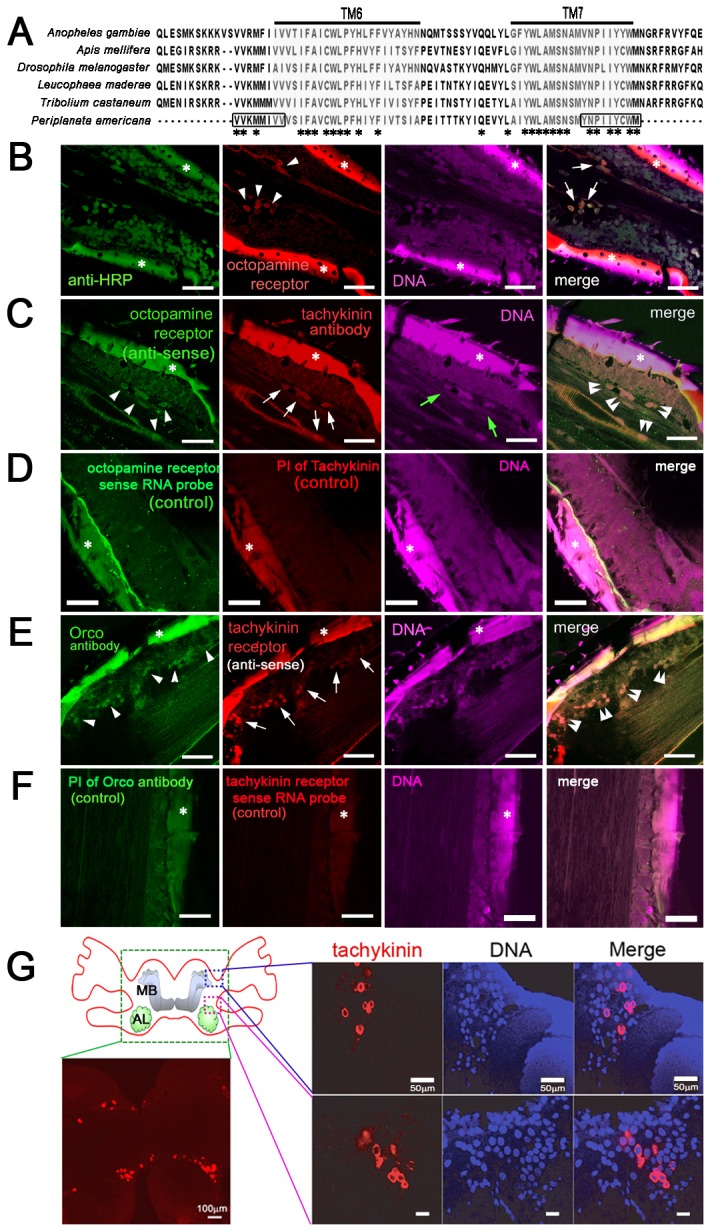
(A) Partial amino acid sequence of tachykinin receptors of Periplaneta americana (PaTKR) and its alignment with other insect tachykinin receptors present in mosquito (Aedes aegypti), honey bee (Apis mellifera), fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster), red flour beetle (Tribolium castaneum), and Madeira cockroach (Leucophaea maderae). Transmembrane regions 6 and 7 are shaded in gray. Amino acid residues selected for gene cloning were indicated by boxes. (B) In situ hybridization with antisense RNA probes of octopamine receptor (red), where octopamine receptors (arrowheads) were co-localized with neuronal marker anti-HRP antibody (arrows). (C) Expression of tachykinin (arrows) in octopamine receptor neurons (green, arrowheads) were co-localized (double arrowheads). Green arrows indicate antennal nerves. (D) Control of in situ hybridization using sense RNA probes of octopamine receptor and pre-immune serum of tachykinin. (E) Tachykinin receptor (arrows) of P. americana was co-localized (double arrowheads) with odorant receptor co-receptor (Orco, arrowheads) in olfactory sensory neurons of the antennae. (F) Control of in situ hybridization using sense RNA probes of tachykinin receptor and pre-immune serum of Orco. Scale bars demonstrate 20 μm. (G) Immunostaining with tachykinin antibody in brain tissue of cockroach. A schematic diagram of the cockroach brain showed mushroom body (MB) and antennal lobes (AL) where tachykinin (red) was mainly localized. Images demonstrate tachykinin staining in the brain area indicated with a dotted box. Cell bodies were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars demonstrate 20 μm unless indicated. Asterisks demonstrate the autofluorescence from antennal cuticle.
