Figure 1. Radiation-responsive miRNAs predicted by miRStress are biologically relevant.
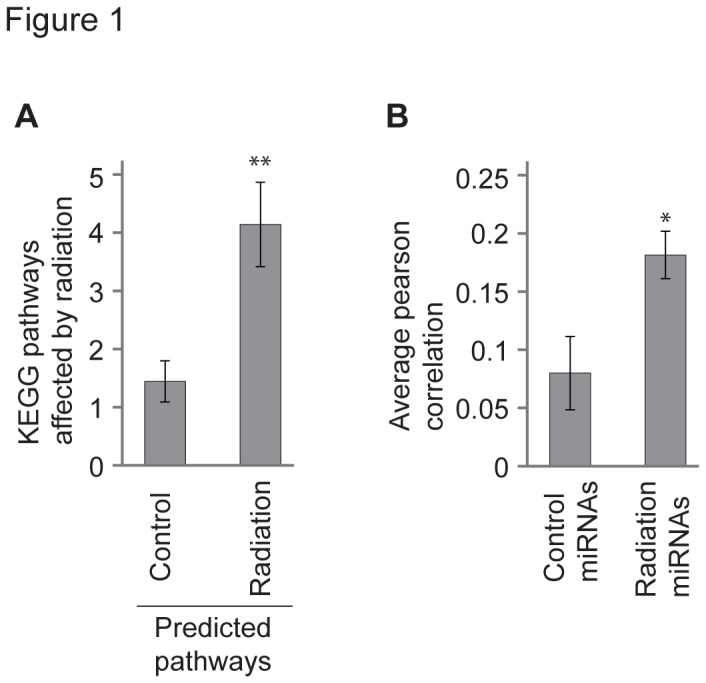
A: The miRNAs which are most frequently deregulated following radiation stress, as reported by miRStress, were used to ‘predict’ radiation-responsive pathways, as described in the methods. Control pathways were selected by using a list of control miRNAs. These were then compared to a list of KEGG pathways which are observed (as opposed to predicted) to actually change following radiation (in a total of 18 datasets). The average frequency with which the predicted control or radiation pathways appears in the observed pathways is shown. On average the radiation predicted-pathways are more frequently present in the observed pathways (t test, p 0.002). In other words, the radiation miRNAs are predicted to target pathways which actually change following radiation. Error bars show standard error of the mean for 20 (for radiation) and 21 (for control) pathways. B: Radiation and control miRNAs used in part A were used to test for correlations between SF5 (surviving fraction of cells following a 5 Gray radiation dose) and miRNA level across the NCI-60 panel. A Pearson correlation was obtained for each radiation and control miRNA (not all were available on the microarray platform). The average Pearson correlation value (see methods) for the control and radiation miRNAs is shown. The radiation miRNAs have a significantly higher correlation with radiosensitivity compared to the control miRNAs (t test, p = 0.02).
