Figure 3. The myo2-E1 mutation targets a highly conserved residue in the myosin motor domain.
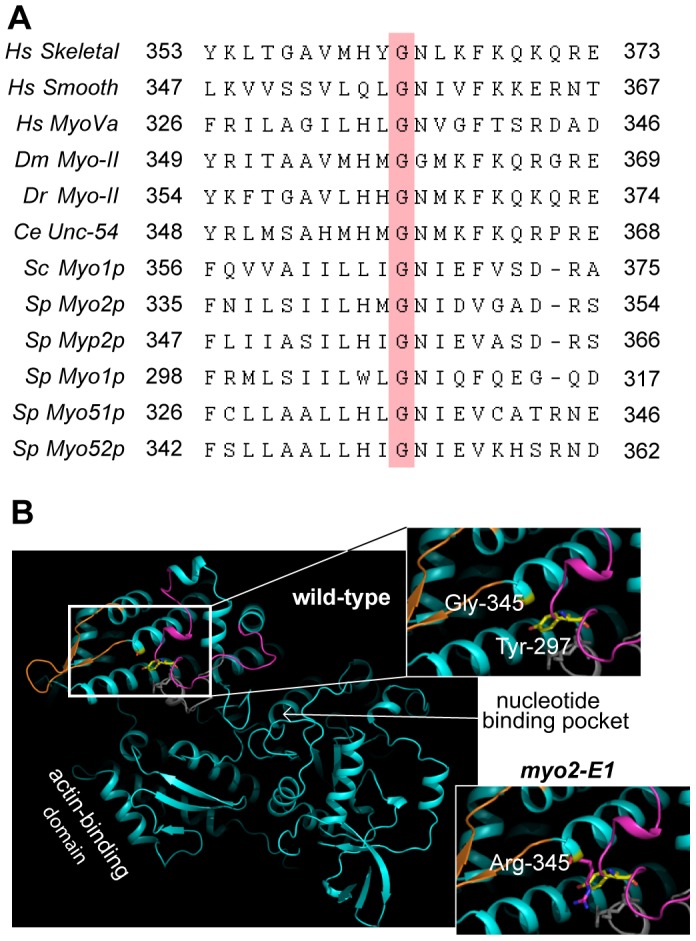
A) Amino acid sequence alignment (centered on Gly-345 of Myo2p) of a number of different myosins. The alignment shows that the glycine residue (pink bar) corresponding to the amino acid substitution in myo2-E1 (G345R) is a highly conserved residue found throughout the myosin super-family. Hs: Homo sapiens, Dm: Drosophila melanogaster, Dr: Danio rerio, Ce: Caenorhabditis elegans, Sc: Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Sp: Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Skeletal and smooth refer to muscle myosin-IIs; Unc-54 is a myosin-II from C. elegans. B) Homology model of the wild-type Myo2p motor based on the 1br4 crystal structure of smooth muscle myosin-II [53]. Insets highlight the area around the site of the -E1 mutation (G345R) in wild-type and myo2-E1-based structures. The potential introduction of a steric clash between Arg-345 and a conserved tyrosine (Tyr-297) is shown in the myo2-E1 inset.
