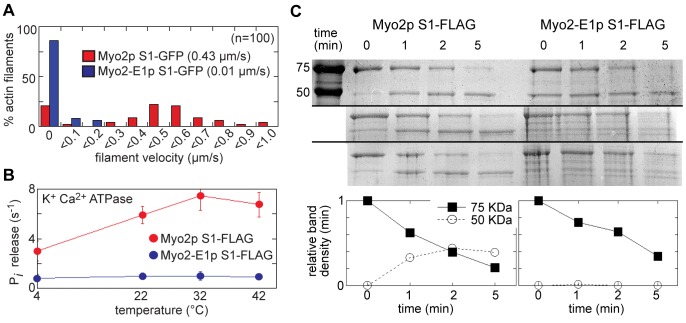
Figure 4. Myo2-E1p motors lack activity and stability.
The function of S1 fragments of wild-type Myo2p and -E1 motors were compared in vitro following their over-expression and isolation from fission yeast. A) Histogram comparing the distribution of motility rates of S1-GFP constructs in actin filament gliding assays. Average values are shown inset (0.43±0.05 µm/s for wild-type; 0.01±0.02 µm/s for -E1). B) The ATPase activity of S1-FLAG constructs was assayed and compared over a range of temperatures in the absence of actin and the presence of high salt (0.5 M KCl) with 10 mM CaCl2. (n = 3). C) S1-FLAG proteins were subjected to limited proteolysis by trypsin and then run on SDS-PAGE gels. The results of three independent proteolysis experiments are shown. Samples were taken at 0, 1, 2, and 5 minutes following the addition of trypsin before proteolysis was stopped by the addition of SDS-PAGE sample buffer. The far left lane in the top gel shows the running position of 75 and 50 KDa molecular weight standards, bands which run at the same position as the undigested S1 heavy chain band and its primary breakdown product respectively. The intensity of the Coomassie-stained undigested S1 (75 KDa band) and its breakdown product (50 KDa band) were quantified by densitometry. Signals were normalized by setting the intensity of the 75 KDa band to 1.0 and the 50 KDa band to 0 at the 0 min time point. The plot shows the average densitometry values for both the 75 KDa and 50 KDa bands from the three experiments.