Figure 3.
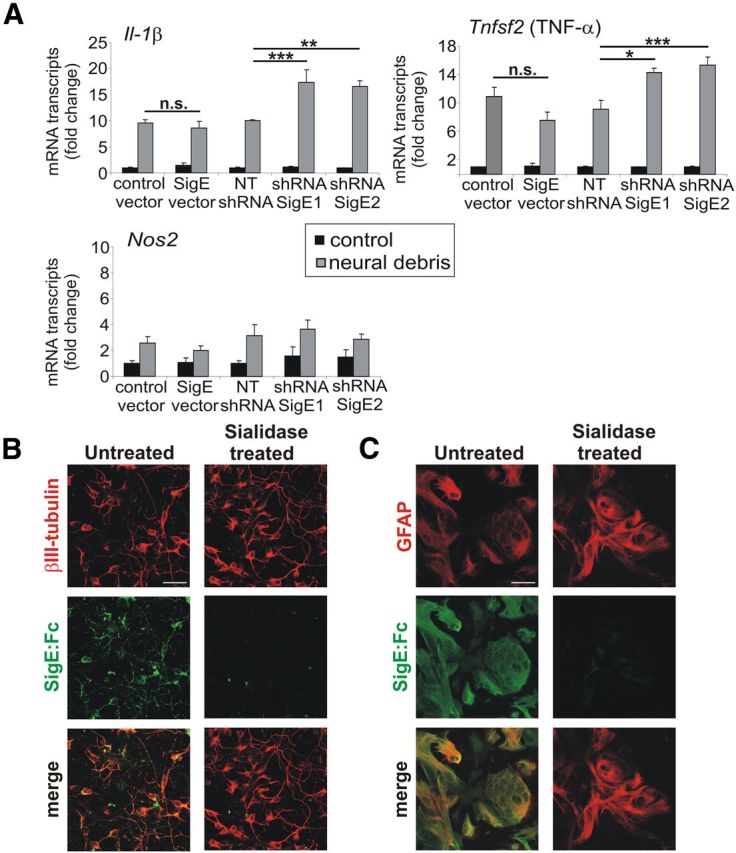
Siglec-E has anti-inflammatory effects and binds to neurons and astrocytes. A, qRT-PCR to detect Il-1β, Tnfsf2 (TNF-α), and Nos2 cDNA after 16 h incubation of microglia with neural debris. Microglia with knockdown of Siglece (shRNASigE1, shRNASigE2) showed a significant increase in gene transcription of Il-1β and Tnfsf2 (TNF-α) in the presence of neural debris compared with the control vector (NTshRNA). *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001; n.s., not significant. B, C, Binding of Siglec-E to sialic acid residues of neural cells. Neurons/astrocytes were either untreated or treated with sialidase and then incubated with the Siglec-E:Fc fusion protein. Removal of sialic acids led to a decreased binding of Siglec-E:Fc to neurons (B) and astrocytes (C). Representative images of three independent experiments are shown. Scale bar, 30 μm.
