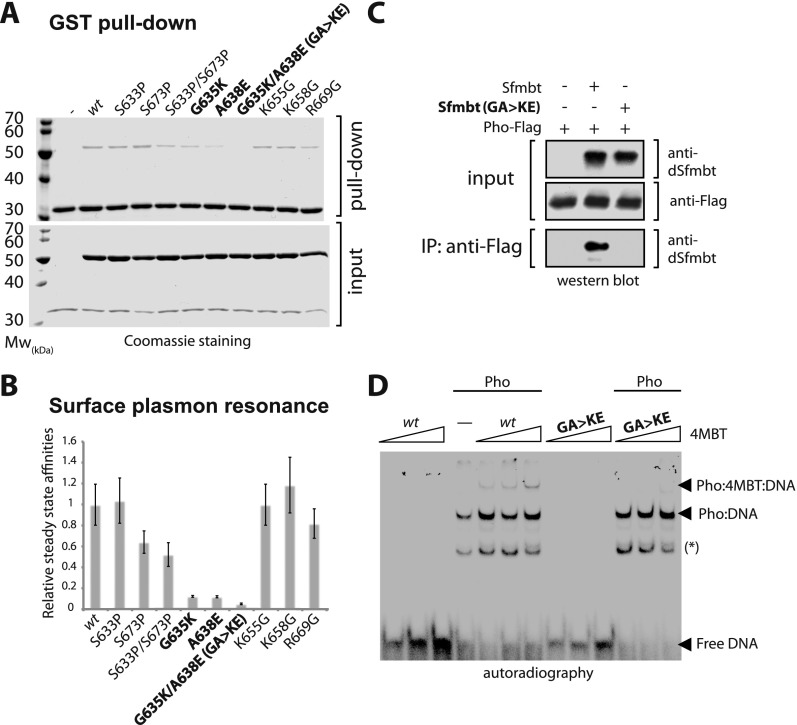
Figure 2.
In vitro mutagenesis analysis of the Pho:Sfmbt interaction. (A) GST pull-down of recombinant GST-Pho spacer and untagged Sfmbt 4MBT wild-type and structure-based mutant proteins. (B) SPR measurements of biotin-labeled Pho and Sfmbt 4MBT wild-type or mutant proteins. Results are shown as affinities relative to the Pho spacer:Sfmbt 4MBT wild-type affinity. (C) Anti-Flag affinity purifications of full-length Pho-Flag:Sfmbt wild-type or mutant complexes detected by Western blot. Antibodies used for the detection are indicated at right. (D) EMSA experiments of full-length Pho or full-length Pho:Sfmbt 4MBT wild-type and mutant complexes using a 32P end-labeled double-stranded Pho DNA-binding site. Arrows indicate full-length Pho:DNA and supershifted Pho:Sfmbt 4MBT:DNA complexes. Lanes containing only DNA and the Sfmbt 4MBT domain were used as control. The asterisk indicates the Pho DNA-binding domain/DNA complex resulting from the degradation of full-length Pho protein as confirmed by mass spectrometry (MS) (data not shown). Binding reactions were performed with 5 ng of DNA probe and 50 ng of Pho full-length protein; 50-fold, 100-fold, and 500-fold molar excess of Sfmbt 4MBT wild-type or mutant protein was added to fixed amounts of Pho protein.