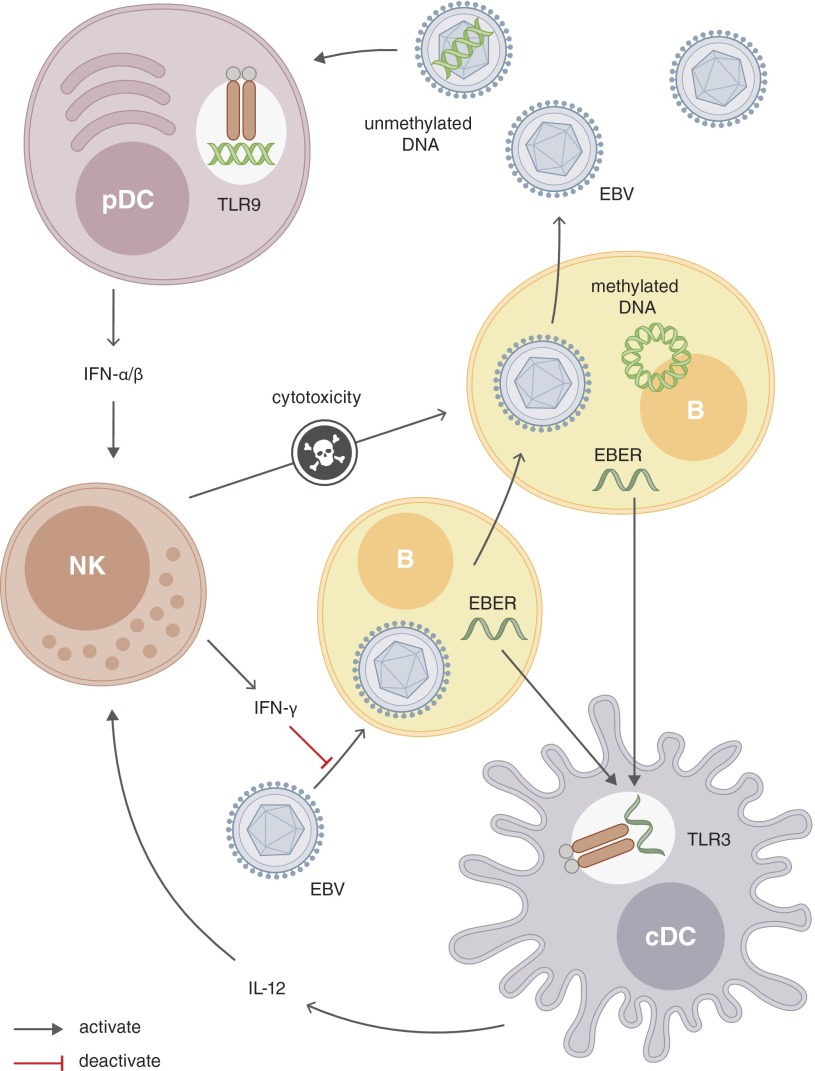
Figure 1. Innate immune recognition via identified PRR ligands and innate restriction of EBV.
EBV seems to activate pDCs and cDCs with its unmethylated viral DNA and EBER, respectively. These pathogen-associated patterns engage TLR9 on pDCs and TLR3 on cDCs. NK cells, which can be activated by pDCs and cDCs to produce IFN-γ in response mainly to IL-12 and increase cytotoxicity upon encountering IFN-α/β, can restrict EBV infection. NK cells prevent B cell transformation via IFN-γ and kill lytically EBV-replicating cells.