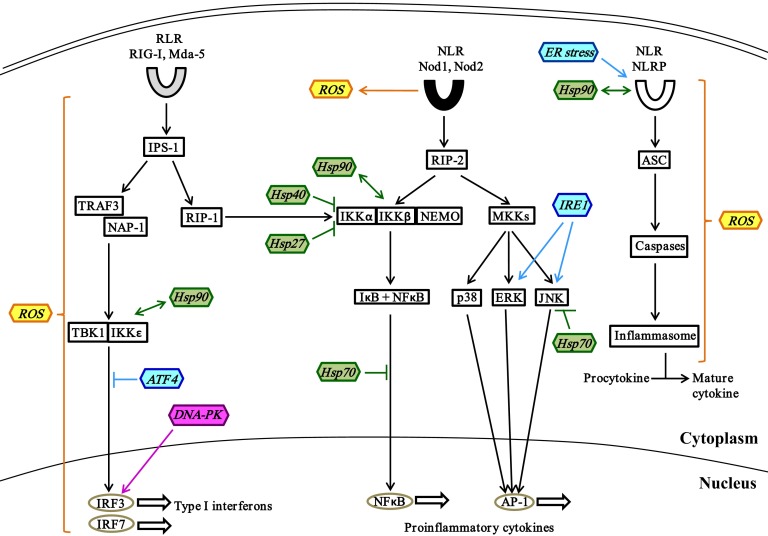
Figure 3. Stress proteins in crosstalk with cytoplasmic PRR signaling.
Activation of cytoplasmic RLRs by viral RNA leads to IRF3- and -7-mediated induction of type I IFNs via the IPS-1–TRAF3–TBK1 pathway. DNA-PK, a DDR protein, can also act as a cytoplasmic PRR to induce expression of type I IFNs. IPS-1-activated RIP-1 also induces the expression of proinflammatory cytokines by activating the NF-κB pathway. The recognition of bacterial peptidoglycans by the NLRs Nod1 and -2 upregulates the expression of proinflammatory cytokines via activation of NF-κB and MKK pathways. Cytoplasmic NLRPs induce activation of inflammasomes via ASC and caspases and is essential for processing of procytokines into their active forms. The crosstalk of stress proteins generated by oxidative stress (yellow), heat shock response (green), UPR (blue), DDR (pink) and cytoplasmic PRR signaling is illustrated. →, stimulation; ↔, direct interaction; ⫞, inhibition.