Abstract
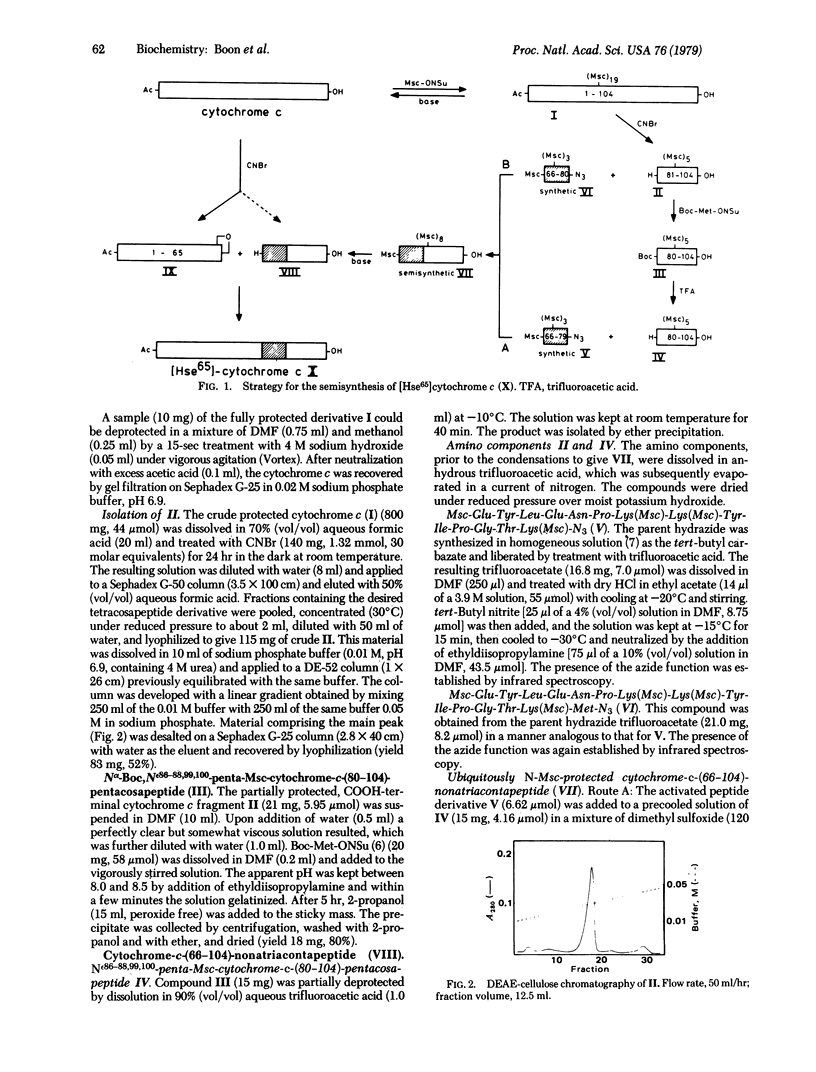
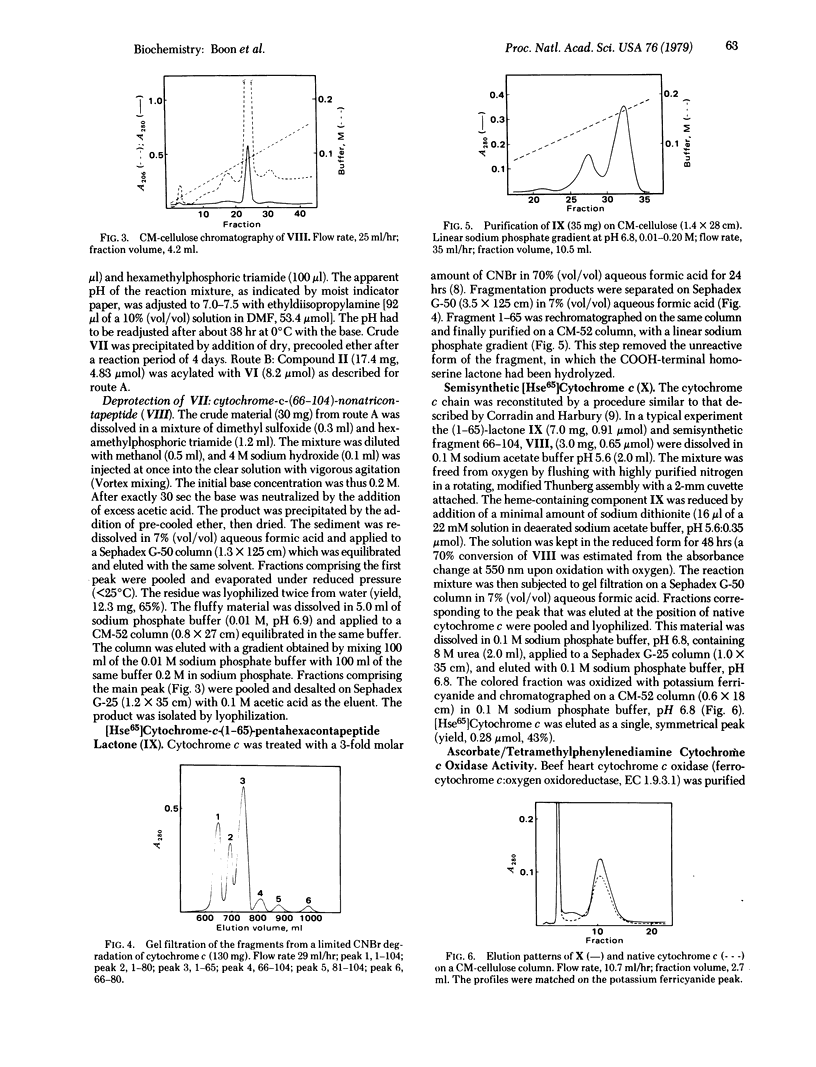
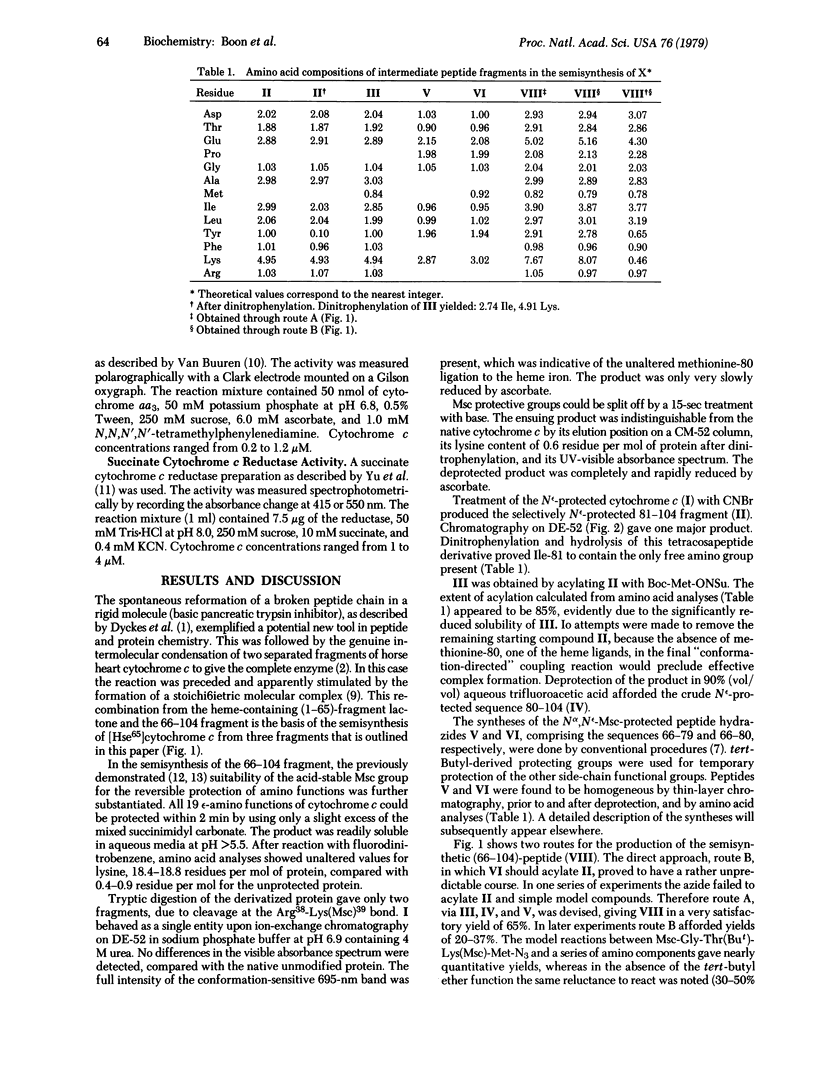
Horse heart cytochrome c was treated with methylsulfonylethyloxycarbonyl succinimide (Msc-ONSu) to give fully Nε-protected cytochrome c. Treatment of this derivative with a hard base for 15 sec regenerated the native tetrahectapeptide chain. CNBr degradation of the protected compound produced three fragments bearing only protective Msc functions on ε-amino groups. The fragment comprising the sequence 81-104 was isolated from the mixture and acylated with N-hydroxysuccinimidyl-t-butyloxycarbonyl-L-methioninate. The resulting pentacosapeptide derivative was partially deprotected by treatment with acid and condensed in good yield (65%) with fully synthetic Nα66, Nε72,73,79- tetra-Msc-cytochrome-c-(66-79)-tetradecapeptide azide. This pathway is preferred because the pentadecapeptide azide derivative 66-80 acylated the Nε-protected tetracosapeptide sequence 81-104 in an unpredictable manner. Subsequent treatment of the product with a base produced unprotected semisynthetic cytochrome-c-(66-104)-nonatriacontapeptide, which is known to undergo acylation by unprotected [Hse65]cytochrome-c-(1-65)-pentahexacontapeptide lactone. The high specificity of this condensation is ascribed to “conformation direction.” Semisynthetic [Hse65]cytochrome c thus prepared reacts like native cytochrome c with a succinate cytochrome c reductase preparation and with cytochrome c oxidase (ferrocytochrome c:oxygen oxidoreductase, EC 1.9.3.1). This semisynthetic strategy may provide a rapid route for the production of cytochrome c analogs modified in the highly conservative sequence 66-80.
Keywords: peptide synthesis, reversible protection, heme protein, conformation direction
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barstow L. E., Young R. S., Yakali E., Sharp J. J., O'Brien J. C., Berman P. W., Harbury H. A. Semisynthetic cytochrome c. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4248–4250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corradin G., Harbury H. A. Cleavage of cytochrome c with cyanogen bromide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Dec 22;221(3):489–496. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corradin G., Harbury H. A. Reconstitution of horse heart cytochrome c: interaction of the components obtained upon cleavage of the peptide bond following methionine residue 65. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3036–3039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corradin G., Harbury H. A. Reconstitution of horse heart cytochrome c: reformation of the peptide bond linking residues 65 and 66. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1400–1406. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyckes D. F., Creighton T., Sheppard R. C. Spontaneous re-formation of a broken peptide chain. Nature. 1974 Jan 25;247(5438):202–204. doi: 10.1038/247202a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson-Miller S., Brautigan D. L., Margoliash E. Correlation of the kinetics of electron transfer activity of various eukaryotic cytochromes c with binding to mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 25;251(4):1104–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsoyannis P. G., Schwartz G. P. The synthesis of peptides by homogeneous solution procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:501–578. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L., Davies H. C., Nava M. Oxidation and reduction of soluble cytochrome c by membrane-bound oxidase and reductase systems. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 10;249(9):2904–2910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesser G. I., Balvert-Geers I. C. The methylsulfonylethyloxycarbonyl group, a new and versatile amino protective function. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1975;7(4):295–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1975.tb02444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Nispen J. W., Smeets P. J., Poll E. H., Tesser G. I. Investigation of the role of tryptophan in alpha-MSH. Replacement by L-pentamethylphenylalanine and L-phenylalanine. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1977;9(3):203–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C. A., Yu L., King T. E. Preparation and properties of cardiac cytochrome c 1 . J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1012–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van GELDER B., SLATER E. C. The extinction coefficient of cytochrome c. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Apr 23;58:593–595. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


