Figure 1.
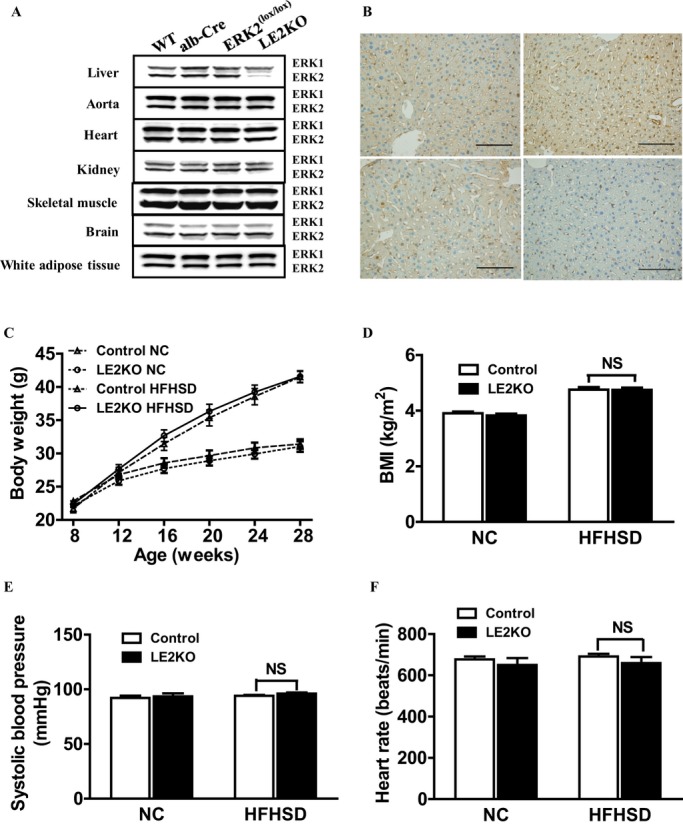
Efficiency of ERK2 deletion and characteristics of LE2KO. (A) ERK1/2 expression in the indicated tissues as detected by western blotting at 8 weeks of age. (B) Immunohistochemistry with anti‐ERK2 antibody in livers from the WT (upper left), Alb‐Cre (upper right), ERK2(lox/lox) (lower left), and LE2KO (lower right) at 8 weeks of age. Scale bars, 100 μm. (C) Weight curves for controls and LE2KO on NC or HFHSD, respectively (n=13 for each group). (D–F) BMI (D) (n=13 for each group), systolic blood pressure (E) (controls on NC; n=5, LE2KO on NC; n=5, controls on HFHSD; n=6, LE2KO on HFHSD; n=6), and heart rate (F) (controls on NC; n=5, LE2KO on NC; n=5, controls on HFHSD; n=6, LE2KO on HFHSD; n=6) in controls and LE2KO on NC or HFHSD, respectively. Error bars represent SEM. Alb‐Cre indicates An albumin promoter–driven Cre recombinase transgenic mouse; BMI, body mass index; ERK, extracellular signal‐regulated kinase; HFHSD, high‐fat/high‐sucrose diet; LE2KO, liver‐specific ERK2 knockout mice; NC, normal chow; WT, wild‐type.
