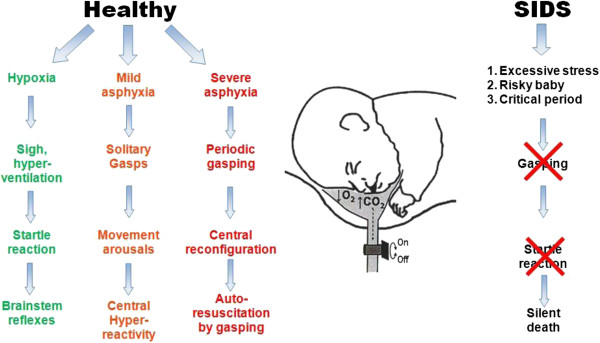
Figure 1.
Autoresuscitation by gasping in healthy infant and its failure in neonate with SIDS. In a normal infant an inhalation of lower O2 and/or higher CO2 content in air evokes hypoxia with occurrence of solitary sighs or gasps. The sigh is accompanied by a startle reaction, which manifests with neck extension and upper airway dilation, resulting in normalization of breathing. Severe hypoxia provokes solitary gasps accompanied by cortical arousal and movements. Progressive asphyxia provokes a period of gasping respiration contributing to autoresuscitation by gasping. Similar asphyxia in a risky preterm baby (including SIDS during a critical period after birth), does not evoke solitary sighs with startle or gasps, but results in silent death. Reproduced with permission and modified from [31].