Fig. 4.
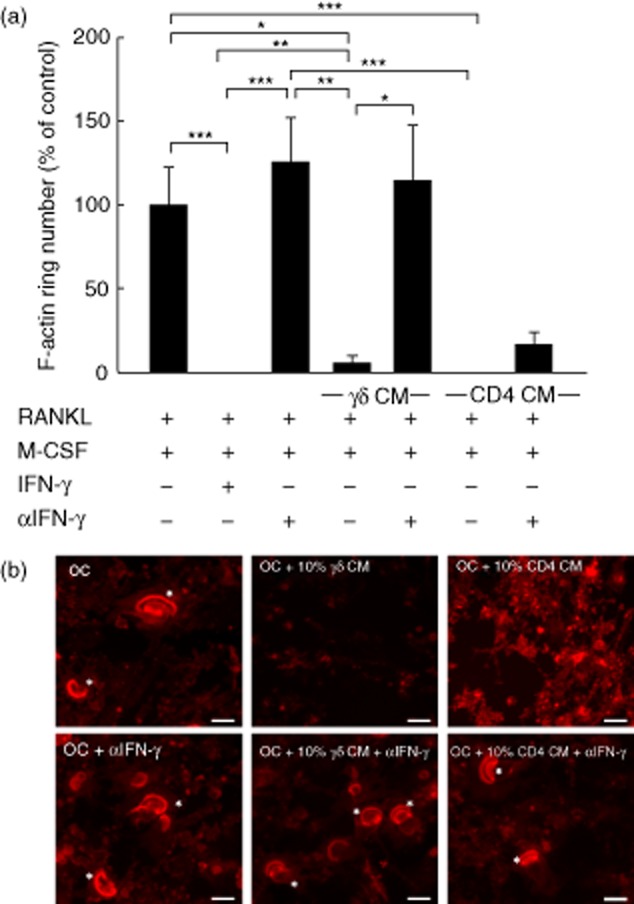
F-actin ring formation in osteoclasts is disrupted by interferon (IFN)-γ derived from activated γδ T cells. Mature osteoclasts were seeded onto dentine discs, supplemented with receptor activator of nuclear factor κB-ligand (RANKL) and macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), and treated with 10% (v/v) conditioned medium (CM) from activated γδ or CD4+ T cells, in the presence or absence of α-IFN-γ, for 6 days. (a) F-actin ring number was quantified by fluorescence microscopy following immunohistochemical staining using tetramethylrhodamineisothiocyanate (TRITC)-phalloidin. Data shown are the mean ± standard error of the mean from three experiments from independent donors. *P < 0·05; **P < 0·05; ***P < 0·001). (b) Representative images of osteoclasts (left panels) treated with CM from activated γδ (middle panels) or CD4+ T cells (right panels), in the presence or absence of α-interferon (IFN)-γ. Asterisks indicate the F-actin rings. Images are from one experiment and are representative of two further experiments from independent donors. Scale bar = 50 μM.
