Fig. 1.
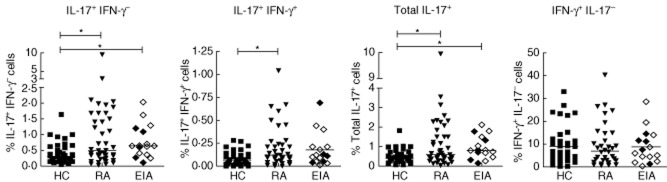
Interleukin (IL)-17+CD4+ T cell frequencies are increased in early inflammatory arthritis (EIA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were isolated by density gradient separation and plated at a density of 1 × 106 with phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) and ionomycin in the presence of GolgiStop for 3 h prior to staining for CD3, CD4, IL-17 and interferon (IFN)-γ. Symbols represent individual patients and lines median values. Between-group comparisons were performed using the Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn's post-test (versus healthy controls). A number of patients within the EIA group could be classified at baseline as RA using the 1987 criteria, shown by open symbols; those with undifferentiated arthritis (UA) are designated by closed symbols within the EIA group. *P < 0·05.
