Fig 3.
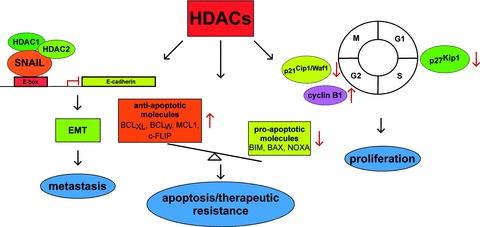
Characterized pathways engaged by HDACs in PDAC. Three molecular well characterized HDAC controlled processes in PDAC are illustrated. Left part: A HDAC1, 2 containing repressor complex is recruited to the E-box of the E-cadherin promoter by the transcription factor SNAIL, contributing to EMT and metastasis. Middle part: HDACs contribute to the imbalanced expression of anti-apoptotic (BCLXL, BCLw, MCL1, c-Flip) and pro-apoptotic (BIM, BAX, NOXA) genes, contributing to apop totic and therapeutic resistance of PDAC cells. Right part: HDACs control expression of the CDKI p21Cip1/Waf1 and cyclin B1 to control G2/M-phase or the CDKI p27Kip1 to control G1/S-phase of the cell cycle.
