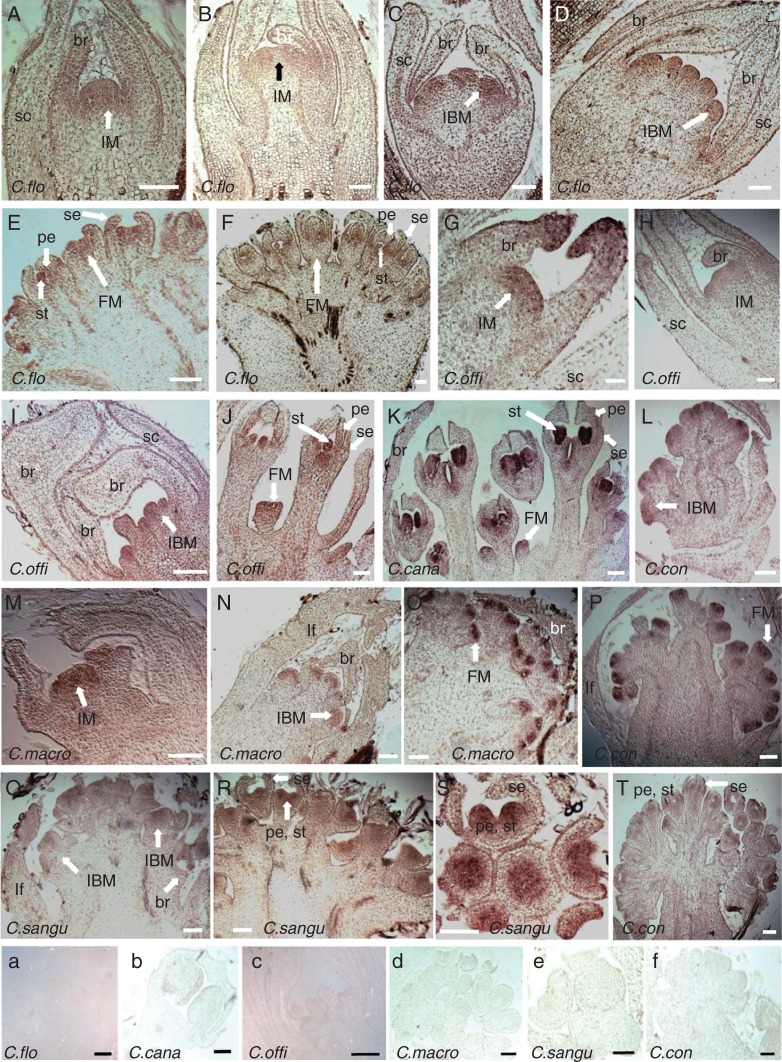
Fig. 4.
Expression pattern of CorLFY in early developmental stages of Cornus inflorescences detected by in situ RNA hybridization. (A–F) Expression of CorLFY in developing inflorescence primordia (IM, IBM, FM, br, se, pe, st) of C. florida. (G–J) Expression of CorLFY in developing inflorescence primordia (IM, IBM, FM, br, se, pe, st) of C. officinalis. (K) Expression of CorLFY in developing inflorescence primordia (FM, se, pe, st) of C. canadensis. (M–O) Expression of CorLFY in developing inflorescence primordia (IM, IBM, FM) meristems of C. macrophylla. (L, P, T) Expression of CorLFY in developing inflorescence meristems (IBM, FM, se, pe, st) of C. controversa. (Q–S) Expression of CorLFY in developing inflorescence primordia (IBM, FM, br, se, pe, st) of C. sanguinea. (a–f) Negative control of CorLFY expression in the six Cornus species: (a) inflorescence meristem of C. florida, comparable to (E); (b) young flower bud of C. canadensis, comparable to one of those in (K); (c) inflorescence branch meristems, comparable to stage in (I); (d) young flower bud of C. macrophylla, comparable to stage in (O); (e) young flower bud of C. sanguinea, comparable to stage in (S); (f) floral meristem of C. controversa, comparable to stage in (P). VM, vegetative meristem; IM, inflorescence meristem; IBM, inflorescence branch meristem; FM, flower meristem; C. flo, C. florida; C. cana, C. canadensis; C. offi, C. officinalis; C. macro, C. macrophylla; C. sangu, C. sanguinea; C. con, C. controversa; lf, leaf; br, bract; se, sepal; pe, petal; st, stamen; sc, scale. Scale bars = 100 μm.