Fig 3.
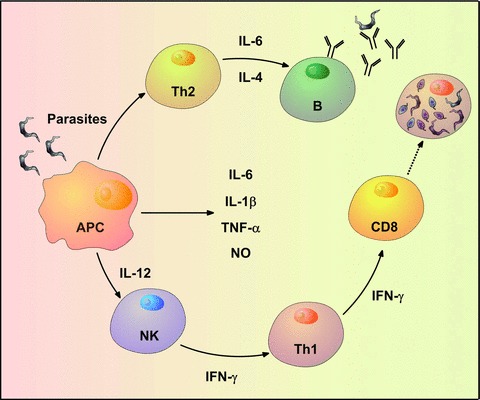
Schematic representation of the protective immune response during T. cruzi acute infection. Antigen-presenting cells are among the first cells that become infected by the trypomastigotes when they enter the mammalian host. Normally, the cells react by up-regulating IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-12 and nitric oxide in an attempt to control the infection. NK cells are among the first line of responders and usually produce high levels of IFN-γ when stimulated by IL-12. The stimulus of the Th1 profile and the CD8+ T cells contributes to eliminate the intracellular amastigotes in infected tissues. On the other hand, the parasite antigens stimulate a Th2 profile which contributes to the production of specific antibodies.
