Fig 4.
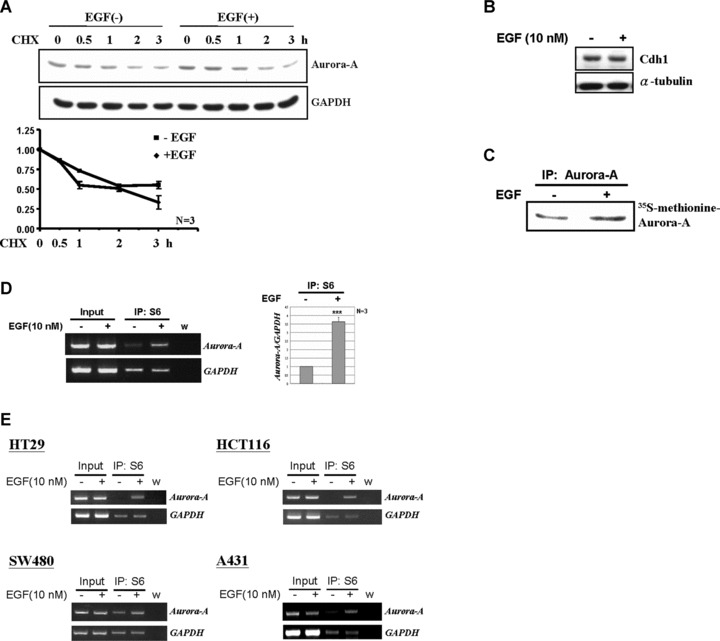
EGF increases the translational efficiency of Aurora-A mRNA. (A) LS174T cells were treated with EGF (10 nM) for 2 hrs and then further incubated with the translational inhibitor, cyclohexamide (CHX, 0.2 μg/ml), for additional 0, 0.5, 1, 2 and 3 hrs. The protein level of Aurora-A was measured by Western blot analysis. Relative protein levels of Aurora-A were normalized to GAPDH. And the quantitative results from three independent experiments was shown below. (B) The expression level of Cdh1 under EGF treated (+) or not (–) was examined by Western blot analysis. (C) 35S-methionine labelled Aurora-A was immunoprecipitated from LS174T cell lysates by anti-Aurora-A antibodies. The immunoprecipitated product was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE and analysed by radiography. (D) Equal amounts of EGF-stimulated cell lysates were used for the ribosomal protein S6-immunoprecipitation assay. The amount of Aurora-A mRNA in the S6-IP complex was analysed by RT-PCR. Quantitative results are shown in the right panel. The mean ± S.D. was obtained from three independent experiments. (w, water control; ***, P < 0.001). (E) Amounts of Aurora A mRNA in the S6-IP complexes of SW480, HT29, HCT116 and A431 cells were analysed as described in (C). (w, water control).
