Fig 1.
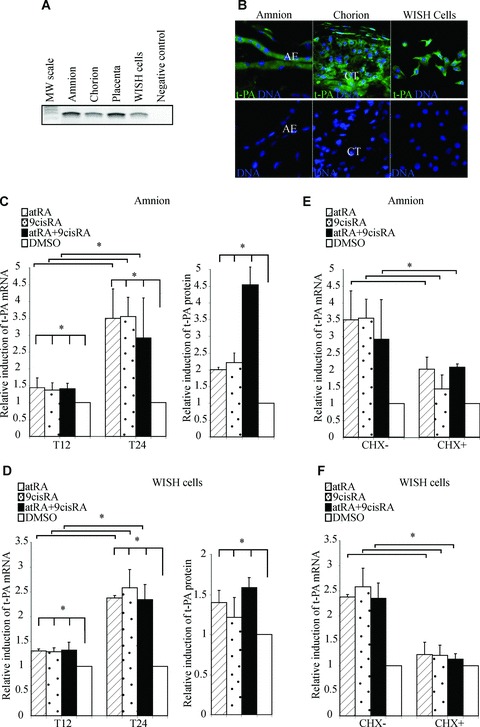
Retinoids up-regulate t-PA mRNA expression and proteins in human amniotic membrane and WISH cells. (A) First-strands cDNA prepared from the amnion, chorion, placenta and WISH cells were used to amplify t-PA mRNA. The observed RT-PCR product matched the size expected (243 pb). The PCR-negative control lane was performed without cDNA. (B) Representative immunofluorescence staining for t-PA protein on foetal membranes and WISH cells. t-PA protein was detected with an anti-t-PA polyclonal antibody recognized by an HRP-labelled secondary antibody and was revealed by a fluorescence amplification system (green). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). AE, amniotic epithelium; CT, chorionic cytotrophoblasts. (C and D) The amnion (C) and WISH cells (D) were treated with 10−6 M atRA and/or 9cisRA for 12 and 24 hrs. Left panel: Total RNA was isolated and subjected to qPCR for t-PA transcript quantification. Right panel: t-PA protein concentrations were measured in cell extracts by ELISA, as described in the Materials and Methods section, and were normalized to total proteins extract concentrations. (E and F) The amnion (E) and WISH cells (F) were treated with or without cycloheximide (CHX), 10−6 M atRA and/or 9cisRA for 24 hrs. In all experiments, t-PA mRNA level was normalized to 36B4 and expressed as the level of induction relative to the control treatment (DMSO). First-strand cDNA was prepared from RNA and equal amounts were subjected to qRT-PCR analysis. Data reported are representative of three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. Each bar gives means ± S.D. *P < 0.05.
