Fig 2.
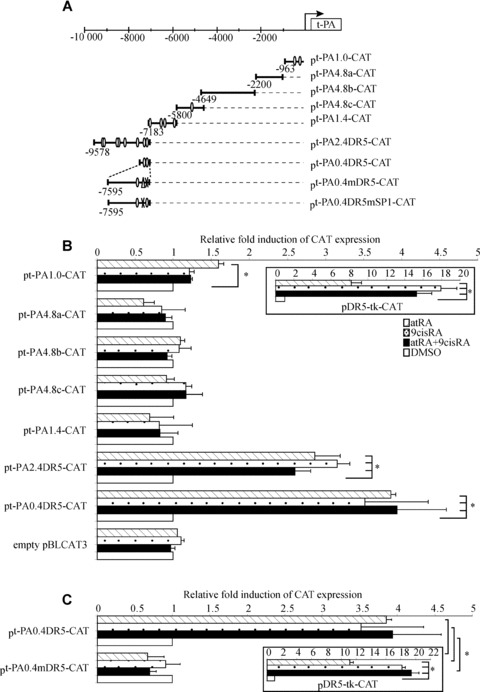
t-PA gene promoter contains a functional DR5 response element located at –7 kb. (A) Schematic representation of different constructs of the t-PA gene promoter. The t-PA promoter contains putative retinoid response elements (open circle) and a putative SP1 fixation site sequence (open triangle). (B) WISH cells were transfected with plasmid containing different lengths of the t-PA gene promoter in combination with the human RAR-α/RXR-α expression vectors pSG5-hRAR-α and pSVL-hRXR-α and then exposed to 10−6 M atRA and/or 9cisRA for 24 hrs. (C) Site-directed mutagenesis analysis of the putative DR5 sequence in the t-PA promoter. WISH cells were transiently transfected with wild-type pt-PA0.4DR5 or mutant pt-PA0.4mDR5 with the human RAR-α/RXR-α expression vectors exposed to 10−6 M atRA and/or 9cisRA for 24 hrs. Positive control was performed using a construct containing a double DR5 linked to thymidine kinase (boxed illustrations). Results are expressed as fold induction relative to the control treatment sample. Each value represents the mean ± S.D. of three separate transfections, each performed in duplicate. *P < 0.05.
