Fig 3.
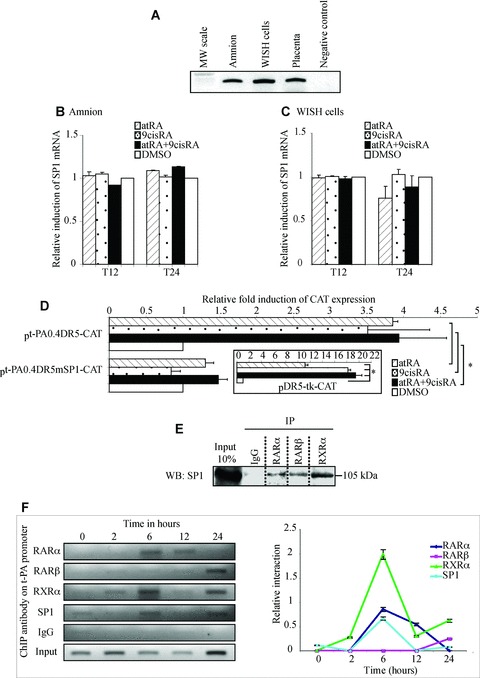
SP1 is necessary in retinoid-mediated regulation of the t-PA gene. (A) First-strand cDNA prepared from the amnion, WISH cells and placenta were used to amplify SP1 mRNA. Placenta cDNA sample was used as a positive control. The observed RT-PCR product matched the expected size (300 pb). (B and C) The amnion (B) and WISH cells (C) were treated with 10−6 M atRA and/or 9cisRA for 12 and 24 hrs. Total RNA was isolated and subjected to qPCR for SP1 transcript quantification. First-strand cDNA was prepared from RNA and equal amounts were subjected to qRT-PCR analysis. In all experiments, SP1 mRNA level was normalized to 36B4 and expressed as the level of induction relative to the control treatment (DMSO). Data reported are representative of three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. Each bar gives mean ± S.D. (D) Site-directed mutagenesis analysis of the putative SP1 sequence in the t-PA promoter. WISH cells were transiently transfected with wild-type pt-PA0.4DR5-CAT or mutant pt-PA0.4mSP1-CAT with the human RAR-α/RXR-α expression vectors exposed to 10−6 M atRA and/or 9cisRA for 24 hrs. For each experiment, a positive control was performed using a construct containing a double DR5 linked to thymidine kinase (boxed illustration). Results are expressed as fold induction relative to the control treatment sample. Each value represents the mean ± S.D. of three separate transfections, each performed in duplicate. *P < 0.05. (E) WISH cells were exposed to 10−6 M atRA and 9cisRA for 24 hrs. Cell lysate proteins were immunoprecipitated with normal rabbit IgG or antibodies raised against RAR-α, RAR-β or RXR-α. Immunoprecipitated proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE, transferred to PVDF membranes and probed with SP1 antibody. Input lane represents 10% of total protein extracts. IP, immunoprecipitation; WB, Western blot. (F) ChIP experiments were performed using WISH cells exposed to 10−6 M atRA and 9cisRA for different times (0, 2, 6, 12 and 24 hrs). Formaldehyde-fixed and sonicated lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation using normal rabbit IgG or antibodies raised against RAR-α, RAR-β, RXR-α or SP1. Non-immunoprecipitated (input) and immunoprecipitated DNA were subjected to PCR using XDR5t-PA primers (151pb; Table 1) that amplify the t-PA promoter region containing DR5 response element and SP1 response element, as described in the Materials and Methods section. Enrichment of immunoprecipitated t-PA chromatin by RARs, RXR-α or SP1 antibodies was specific compared with ChIP performed using IgG control antibodies. Graph represents semi-quantitative relative interaction of RAR-α (lozenge), RAR-β (square), RXR-α (triangle) and SP1 (circle) compared with input control (obtained from n= 3 independent assays).
